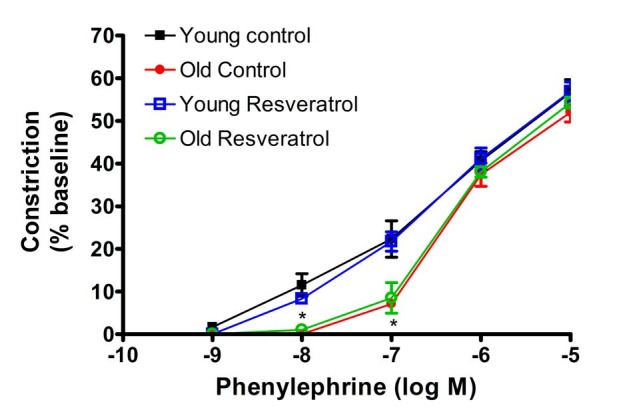
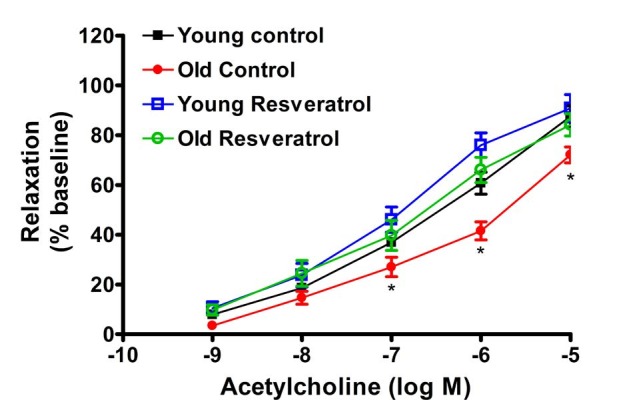
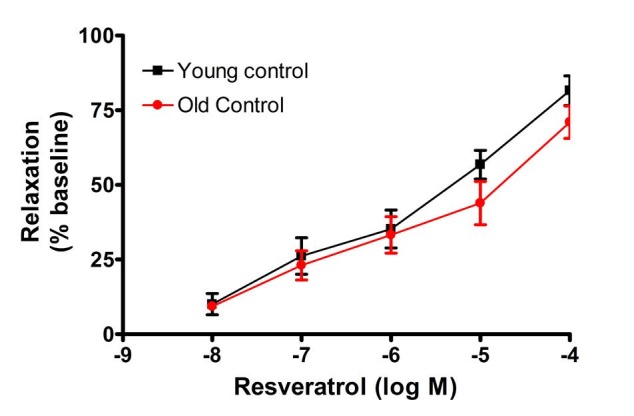
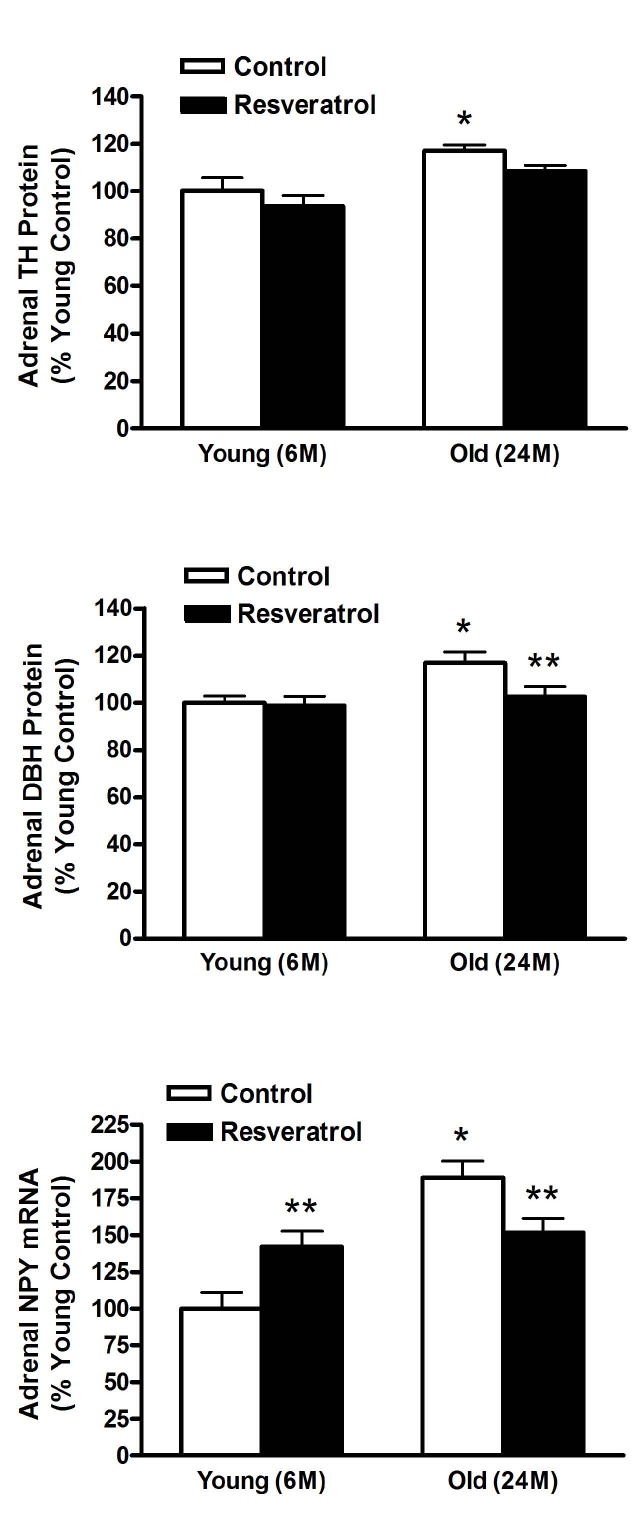
1. Anon. National High Blood Pressure Education Program Working Group Report on Hypertension in the Elderly. National High Blood Pressure Education Program Working Group.
Hypertension. 1994. 23:p. 275-285. PMID:
10.1161/01.HYP.23.3.275. PMID:
8125550.
2. Tuck ML.. Treatment of hypertension in the elderly. et al, Armbrecht JA., Coe R., eds Wongsurawat N.Endocrine function and aging. New York: Springer-Verlag: 1989,. p. 147-160.
3. Virmani R., Avolio AP., Mergner WJ., Robinowitz M., Herderick EE., Cornhill JF., Guo SY., Liu TH., Ou DY., O’Rourke M.. Effect of aging on aortic morphology in populations with high and low prevalence of hypertension and atherosclerosis: comparision between occidental and Chinese communities.
Am J Pathol 1991;139:1119-1129. PMID:
1951629.
4. Lakatta EG., Levy D.. Arterial and cardiac aging: major shareholders in cardiovascular disease enterprises: Part I: aging arteries: a “set up” for vascular disease.
Circulation 2003;107:139-146. PMID:
10.1161/01.CIR.0000048892.83521.58. PMID:
12515756.

5. Csiszar A., Pacher P., Kaley G., Ungvari Z.. Role of oxidative and nitrosative stress, longevity genes and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase in cardiovascular dysfunction associated with aging.
Curr Vasc Pharmacol 2005;3:285-291. PMID:
10.2174/1570161054368616. PMID:
16026324.

6. Egashira K., Inou T., Hirooka Y., Kai H., Sugimachi M., Suzuki S., Kuga T., Urabe Y., Takeshita A.. Effects of age on endothelium-dependent vasodilation of resistance coronary artery by acetylcholine in humans.
Circulation 1993;88:77-81. PMID:
10.1161/01.CIR.88.1.77. PMID:
8319359.

7. Seals DR., Jablonski KL., Donato AJ. .. Aging and vascular endothelial function in humans.
Clin Sci 2011;120:357-375. PMID:
10.1042/CS20100476. PMID:
21244363.


8. Chou TC., Yen MH., Li CY., Ding YA.. Alterations of nitric oxide synthase expression with aging and hypertension in rats.
Hypertension 1998;31:643-648. PMID:
10.1161/01.HYP.31.2.643. PMID:
9461235.

9. Csiszar A., Ungvari Z., Edwards JG., Kaminski P., Wolin MS., Koller A., Kaley G.. Aging-induced phenotypic changes and oxidative stress impair coronary arteriolar function.
Circ Res 2002;90:1159-1166. PMID:
10.1161/01.RES.0000020401.61826.EA. PMID:
12065318.

10. Ferrer M., Sanchez M., Minoves N., Salaices M., Balfagón G.. Aging increases neuronal nitric oxide release and superoxide anion generation in mesenteric arteries from spontaneously hypertensive rats.
J Vasc Res 2003;40:509-519. PMID:
10.1159/000075183. PMID:
14646371.

11. Van der Loo B., Labugger R., Skepper JN., Bachschmid M., Kilo J., Powell JM., Palacios-Callender M., Erusalimsky JD., Quaschning T., Malinski T., Gygi D., Ullrich V., Lüscher TF.. Enhanced peroxynitrite formation is associated with vascular aging.
J Exp Med 2000;192:1731-1744. PMID:
10.1084/jem.192.12.1731. PMID:
11120770.


12. Esler MD., Turner AG., Kaye DM., Thompson JM., Kingwell BA., Morris M., Lambert GW., Jennings GL., Cox HS., Seals DR.. Aging effects on human sympathetic neuronal function.
Am J Physiol 1995;268:R278-R285. PMID:
7840332.

13. Esler M., Hastings J., Lambert G., Kaye D., Jennings G., Seals DR.. The influence of aging on the human sympathetic nervous system and brain norepinephrine turnover.
Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 2002;282:R909-R916. PMID:
10.1152/ajpregu.00335.2001. PMID:
11832414.

14. Seals DR., Dinenno FA.. Collateral damage: cardiovascular consequences of chronic sympathetic activation with human aging.
Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2004;287:H1895-H1905. PMID:
10.1152/ajpheart.00486.2004. PMID:
15475526.

15. Kedzierski W., Porter JC.. Quantitative study of tyrosine hydroxylase mRNA in catecholaminergic neurons and adrenals during development and aging.
Brain Res Mol Brain Res 1990;7:45-51. PMID:
10.1016/0169-328X(90)90072-L. PMID:
1967814.

16. Tumer N., Hale C., Lawler J., Strong R.. Modulation of tyrosine hydroxylase gene expression in the rat adrenal gland by exercise: effects of age.
Brain Res Mol Brain Res 1992;14:51-56. PMID:
10.1016/0169-328X(92)90009-Z. PMID:
1353855.

17. Tumer N., LaRochelle JS.. Tyrosine hydroxylase expression in rat adrenal medulla: influence of age and cold.
Pharmacol Biochem Behav 1995;51:775-780. PMID:
10.1016/0091-3057(95)00030-Z. PMID:
7675858.

18. Voogt JL., Arbogast LA., Quadri SK., Andrews G.. Tyrosine hydroxylase messenger RNA in the hypothalamus, substantia nigra and adrenal medulla of old female rats.
Brain Res Mol Brain Res 1990;8:55-62. PMID:
10.1016/0169-328X(90)90009-3. PMID:
1974316.

19. Erdem SR., Broxson CS., Erdem A., Spar DS., Williams RT., Tümer N.. The age-related discrepancy in the effect of neuropeptide Y on select catecholamine biosynthetic enzymes in the adrenal medulla and hypothalamus in rats.
Neuropharmacology 2002;43:1280-1288. PMID:
10.1016/S0028-3908(02)00293-9. PMID:
12527477.

20. Higuchi H., Yokokawa K., Iwasa A., Yoshida H., Miki N.. Age-dependent increase in neuropeptide Y gene expression in rat adrenal gland and specific brain areas.
J Neurochem 1991;57:1840-1847. PMID:
10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb06393.x. PMID:
1940903.

21. Lundberg JM., Terenius L., Hökfelt T., Martling CR., Tatemoto K., Mutt V., Polak J., Bloom S., Goldstein M.. Neuropeptide Y (NPY)-like immunoreactivity in peripheral noradrenergic neurons and effects of NPY on sympathetic function.
Acta Physiol Scand 1982;116:477-480. PMID:
10.1111/j.1748-1716.1982.tb07171.x. PMID:
6763452.

22. Tumer N., Broxson CS., LaRochelle JS., Scarpace PJ.. Induction of tyrosine hydroxylase and neuropeptide Y by carbachol: modulation with age.
J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 1999;54:B418-B423. PMID:
10.1093/gerona/54.10.B418. PMID:
10568524.


23. Jang M., Cai L., Udeani GO., Slowing KV., Thomas CF., Beecher CW., Fong HH., Farnsworth NR., Kinghorn AD., Mehta RG., Moon RC., Pezzuto JM.. Cancer chemopreventative activity of resveratrol, a natural product derived from grapes.
Science 1997;275:218-220. PMID:
10.1126/science.275.5297.218. PMID:
8985016.

25. Baur JA., Sinclair DA.. Therapeutic potential of resveratrol: the in vivo evidence.
Nat Rev Drug Discov 2006;5:493-506. PMID:
10.1038/nrd2060. PMID:
16732220.


27. Wu JM., Wang ZR., Hsieh TC., Bruder JL., Zou JG., Huang YZ.. Mechanism of cardioprotection by resveratrol, a phenolic antioxidant present in red wine.
Int J Mol Med 2001;8:3-17. PMID:
10.3892/ijmm.8.1.3. PMID:
11408943.

28. Chen CK., Pace-Asciak CR.. Vasorelaxing activity of resveratrol and quercetin in isolated rat aorta.
Gen Pharmacol 1996;27:363-366. PMID:
10.1016/0306-3623(95)02001-2. PMID:
8919657.

29. Naderali EK., Doyle PJ., Williams G.. Resveratrol induces vasorelaxation of mesenteric and uterine arteries from female guinea-pigs.
Clin Sci 2000;98:537-543. PMID:
10.1042/cs0980537. PMID:
10781384.


30. Naderali EK., Smith LH., Doyle JP., Williams G.. The mechanism of resveratrol-induced vasorelaxation differs in the mesenteric resistance arteries of lean and obese rats.
Clin Sci 2001;100:55-60. PMID:
10.1042/cs1000055. PMID:
11115418.


31. Jager U.. Nguyen-Duong H. Relaxant effect of trans resveratrol on isolated porcine coronary arteries.
Arzneimittelforschung 1999;49:207-211. PMID:
10219463.

32. Rakici O., Ugursay K., Coskun B., Aslamaci S., Akar F.. Effects of resveratrol on vascular tone and endothelial function of human saphenous vein and internal mammary artery.
Int J of Cardiol 2005;105:209-215. PMID:
10.1016/j.ijcard.2005.01.013. PMID:
16243115.

34. Rush JW., Quadrilatero J., Levy AS., Ford RJ.. Chronic resveratrol enhances endothelium dependent relaxation but does not alter eNOS level in aorta of spontaneously hypertensive rats. Exp Biol Med 2007;232:814-822.
35. Zhang H., Zhang J., Ungvari Z., Zhang C.. Resveratrol improves endothelial function: role of TNFα and vascular oxidative stress.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2009;29:1164-1171. PMID:
10.1161/ATVBAHA.109.187146. PMID:
19478208.

36. Zou JG., Wang ZR., Huang YZ., Cao KJ., Wu JM.. Effect of red wine and wine polyphenol resveratrol on endothelial function in hypercholesterolemic rabbits.
Int J Mol Med 2003;11:317-320. PMID:
10.3892/ijmm.11.3.317. PMID:
12579333.

37. Soylemez S., Gurdal H., Sepici A., Akar F.. The effect of long-term resveratrol treatment to estrogen in aortae from male and female rats: Role of nitric oxide and superoxide.
Vascular Pharmacol 2008;49:97-105. PMID:
10.1016/j.vph.2008.06.006.

38. Soylemez S., Sepici A., Akar F.. Resveratrol supplementation gender independently improves endothelial reactivity and suppresses superoxide production in healthy rats. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther 2009;23:449-458. PMID:
10.1007/s10557-009-6198-z. PMID:
19809869.



39. Erdos B., Miller AW., Busija DW.. Impaired endothelium-mediated relaxation in isolated cerebral arteries from insulin-resistant rats.
Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2002;282:H2060-H2065. PMID:
10.1152/ajpheart.01124.2001. PMID:
12003812.

40. Novakovic A., Gojkovic-Bukarica L., Peric M., Nezic D., Djukanovic B., Markovic-Lipkovski J., Heinle H.. The mechanism of edothelium-idependent relaxation iduced by the wine polyphenol resveratrol in human internal mammary artery.
J Pharmacol Sci 2006;101:85-90. PMID:
10.1254/jphs.FP0050863. PMID:
16682785.

41. Gojkovic-Bukarica L., Novakovic A., Kanjuh V., Bumbasirevic M., Lesic A., Heinle H.. A role of ion channels in the endothelium-independent relaxation of rat mesenteric artery induced by resveratrol.
J Pharmacol Sci 2008;108:124-130. PMID:
10.1254/jphs.08128FP. PMID:
18818483.

42. Nagaoka T., Hein TW., Yoshida A., Kuo L.. Resveratrol, a component of red wine, elicits dilation of isolated porcine retinal arterioles: Role of nitric oxide and potassium channels.
Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2007;48:4232-4239. PMID:
10.1167/iovs.07-0094. PMID:
17724212.

43. Novakovic A., Gojkovic-Bukarica L., Kanjuh V., Heinle H.. Potassium channels-mediated vasorelaxation of rat aorta induced by resveratrol.
Basic Clin Pharmacol and Toxicol 2006;99:360-364. PMID:
10.1111/j.1742-7843.2006.pto_531.x.

44. Andriambeloson E., Stoclet JC., Andriantsitohaina R.. Mechanism of endothelial nitric oxide-dependent vasorelaxation induced by wine polyphenols in rat thoracic aorta.
J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 1999;33:248-254. PMID:
10.1097/00005344-199902000-00011. PMID:
10028933.

45. Beretz A., Stierle A., Anton R., Cazenave JP.. Role of cyclic AMP in the inhibition of human platelet aggregation by quercetin, a flavonoid that potentiates the effects of prostacyclin.
Biochem Pharmacol 1982;31:3597-3600. PMID:
10.1016/0006-2952(82)90581-0. PMID:
6295405.

46. Smith AR., Visioli F., Hagen TM.. Plasma membrane-associated endothelial nitric oxide synthase and activity in aging rat aortic vascular endothelia markedly decline with age.
Arch Biochem Biophys 2006;454:100-105. PMID:
10.1016/j.abb.2006.02.017. PMID:
16982030.

47. Van der Loo B., Bachschmid M., Labugger R., Schildknecht S., Kilo J., Hahn R., Palacios-Callender M., Lüscher TF.. Expression and activity patterns of nitric oxide synthases and antioxidant enzymes reveal a substantial heterogeneity between cardiac and vascular aging in the rat.
Biogerontology 2005;6:325-334. PMID:
10.1007/s10522-005-4807-1. PMID:
16463109.


48. Bruder JL., Hsieh TC., Lerea KM., Olson SC., Wu JM.. Induced cytoskeletal changes in bovine pulmonary artery endothelial cells by resveratrol and the accompanying modified responses to arterial shear stress.
BMC Cell Biol 2001;2:1-11. PMID:
10.1186/1471-2121-2-1. PMID:
11178103.

49. Hsieh TC., Juan G., Darzynkiewicz Z., Wu JM.. Resveratrol increases nitric oxide synthase, induces accumulation of p53 and p21(WAF1/CIP1), and suppresses cultured bovine pulmonary artery endothelial cell proliferation by perturbing progression through S and G2.
Cancer Res 1999;59:2596-2601. PMID:
10363980.
50. Wallerath T., Deckert G., Ternes T., Anderson H., Li H., Witte K., Förstermann U.. Resveratrol, a polyphenolic phytoalexin present in red wine, enhances expression and activity of endothelial nitric oxide synthase.
Circulation 2002;106:1652-1658. PMID:
10.1161/01.CIR.0000029925.18593.5C. PMID:
12270858.

51. Muller-Delp JM., Gurovich AN., Christou DD., Leeuwenburgh C.. Redox balance in the aging microcirculation: New friends, new foes, and new clinical directions.
Microcirculation 2011;19:19-28. PMID:
10.1111/j.1549-8719.2011.00139.x. PMID:
21954960.

52. Li H., Förstermann U.. Resveratrol: A multifunctional compund improving endothelial function.
Cardiovasc Drugs Ther 2009;23:425-429. PMID:
10.1007/s10557-009-6209-0. PMID:
19937102.


53. Ungvari Z., Orosz Z., Labinskyy N., Rivera A., Xiangmin Z., Smith K., Csiszar A.. Increased mitochondrial H2O2 production promotes endothelial NF-κB activation in aged rat arteries.
Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2007;293:H37-H47. PMID:
10.1152/ajpheart.01346.2006. PMID:
17416599.

54. Csiszar A., Smith K., Labinskyy N., Orosz Z., Rivera A., Ungvari Z.. Resveratrol attenuates TNF-α induced activation of coronary arterial endothelial cells: role of NF-kappaB inhibition.
Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2006;291:H1694-H1699. PMID:
10.1152/ajpheart.00340.2006. PMID:
16973825.

55. Banerji TK., Parkening TA., Collins TJ.. Adrenomedullary catecholaminergic activity increases with age in male laboratory rodents.
J Gerontol 1984;39:264-268. PMID:
10.1093/geronj/39.3.264. PMID:
6715801.


56. Erdos B., Erdem SR., Erdem A., Broxson CS., Tümer N.. Effect of age on angiotensin II-mediated downregulation of adrenomedullary catecholamine biosynthetic enzymes.
Exp Gerontol 2008;43:806-809. PMID:
10.1016/j.exger.2008.04.012. PMID:
18522866.