|
 |
- Search
| Phys Act Nutr > Volume 26(3); 2022 > Article |
|
Abstract
[Purpose]
This study aimed to evaluate the differences between predicted resting energy expenditure (REE), using fat-free mass (FFM)-based prediction equations, and measured REE in Korean male collegiate soccer players.
[Methods]
Fifteen male collegiate soccer players (18-21 years) participated in this study. The REE measurements were conducted using the Douglas bag method. Body composition was measured by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA). The differences between the measured REE and predicted REE, using the five FFM-based REE equations, were analyzed using the t-test, calculation of errors, regression analysis, and the Bland-Altman method.
[Results]
The Cunningham (1980) and ten Haaf and Weijs (2014) equations showed significantly overestimated REE (1,808 ± 99 kcal/d, p <0.01; 1,838 ± 103 kcal/d, p <0.01; respectively), but the Owen (1988), Taguchi (2011), and Kim (2015) equations’ estimations were not significantly different from the measured REE (1,589 ± 106 kcal/d, 1,640 ± 124 kcal/d, and 1,622 ± 68 kcal/d, respectively). The Taguchi equation gave the best prediction of REE with the lowest constant error (-6 ± 125) and effect size (-0.05), and a non-significant proportional bias (p = 0.95).
[Conclusion]
The Taguchi equation is recommended for predicting REE in Korean collegiate soccer players. The selection process of a REE-prediction equation must take into consideration the target population’s characteristics. Future studies are recommended to evaluate the validity of the different FFM-based REE-prediction equations in various Korean athletes.
In athletes, excessive energy expenditure during exercise and training without adequate energy intake can result in energy deficiency [1]. Previous studies have focused on this imbalance between exercise and recovery in athletes, and this has prompted the introduction of the term ‘Relative Energy Deficiency in Sport (RED-S)’ in the International Olympic Committee consensus statement [1,2]. Most initial studies mainly focused on athletes competing in endurance and weight-sensitive sports; however, later studies involving athletes competing in racquet, ball, and team sports (such as soccer) also showed a risk of energy deficiency [1,3-6]. Energy deficiency can trigger disturbances in physiological homeostasis thereby inducing alterations in reproductive and immune functions, anabolic actions (bone and protein synthesis), and metabolism [1]. Furthermore, chronic energy deficiency can result in metabolic adaptations to reduce energy expenditure in order to prevent a decrease in essential tissues and physiological functions [7]. Studies involving athletes during intensified exercise periods revealed less than expected or no changes in body composition with alterations in resting energy expenditure (REE) and metabolic hormones [8,9]. To monitor energy deficiency regardless of metabolic adaptation, the estimation of the ratio between measured REE (REEm) and predicted REE (REEp), the REEratio has been suggested, and the latter has been shown to present significant correlations with energy deficiency, menstrual disorder, and low triiodothyronine level [10-13].
For precise REEratio estimation, it is important to use validated REE measurement and prediction methods. Indirect calorimetry is a widely used validated method that estimates energy metabolism using gas exchange measurements, and it has low error ranges under optimal conditions and preparation [14,15]. However, for the prediction of REE, various equations have been developed from different populations [16-22]. Previous reviews on the effect of race/ethnicity on REE presented differences in REE between African Americans and Caucasians after adjusting for fat-free mass (FFM), and suggested a validation study on REE-prediction equations in different ethnic groups [23,24]. Studies have been conducted to examine the validity of REE-prediction equations in non-athletic Asian populations, and the importance of developing new race/ethnicity-specific equations has been pointed out [25-27]. Furthermore, compared to the general population, athletes have a higher FFM, which consists of metabolically active tissues, and the use of equations that do not account for FFM can result in underestimation of REE in athletes [22]. Previous studies that examined REE-prediction equations in athletes demonstrated that FFM-based equations presented better estimations than body weight (BW)-based equations [28,29]. In addition, a study on the accuracy of REE-prediction equations in Korean athletic and non-athletic adolescents showed that the appropriate equations were different for each group [30].
To the best of our knowledge, a limited number of studies have examined the differences between REEm and REEp among Asian athletes. The validity of previously developed REE-prediction equations have been studied in athletes in Western countries [28,29,31,32]. A Japanese study involving 205 Japanese female athletes suggested a new prediction equation [REE = 27.5 × FFM + 5], and a study involving 100 Korean adolescent athletes and non-athletes also suggested a new FFM-based prediction equation [REE = 15 × FFM + 730.4] [21,30,33,34]. However, the differences between REEp using these equations and REEm have not been examined in Asian athletes. Therefore, this study aimed to compare differences between REEp, using different FFM-based REE-prediction equations, and REEm in Korean male collegiate soccer players.
Fifteen male Korean collegiate soccer players, aged 18-21 years, were recruited from a local university team competing in the Korean National University League (U-League). All participants were non-smokers without any health issues and had exercised for 7-12 years. Data were collected during the training season in October 2018. Participants followed scheduled team training (06:00-08:00 & 15:00-17:00) on weekdays and had rest on the weekends. Some participants voluntarily scheduled additional training sessions. Each participant provided a written informed consent after having been informed of the study design and risks of the experimental procedures. This study was approved by the Human Research Ethics Committee of Waseda University for the use of human subjects in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki (2018-082).
Before the REE measurement, height was measured using a digital stadiometer (BSM 330, Biospace, Seoul, Korea) and BW was measured using a digital scale (UC-321, A&D Medical, Tokyo, Japan). The FFM of participants were measured using a dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) scanner (Lunar Prodigy Advance with enCORE software version 16, GE Healthcare, Wisconsin, USA) by a certified technician.
The REEm was assessed by open-circuit indirect calorimetry using the Douglas bag method. The participants were instructed to avoid strenuous exercise, caffeine, and alcohol for at least 24 h before the measurement, and they arrived at the laboratory next to their dormitory at 07:00 a.m. after an overnight fast. After 20 min of rest in the supine position to get acclimatize with room temperature, participants rested wearing a mask (Hans Rudolph, Kansas, Missouri, USA) and were familiarized with the equipment. The resting heart rate and body temperature were measured to confirm the resting status. After the confirmation, 10 min of expired gas samples were collected in Douglas bags. Oxygen uptake (VO2) and carbon dioxide production (VCO2) were analyzed with a gas analyzer using AE-100i (Minato Medical Science, Osaka, Japan), and the expired volume and temperature were assessed with a dry gas volume meter using DC-5A (Shinagawa, Tokyo, Japan). REEm was calculated using the Weir equation: 3.94 × (VO2) + 1.1 × (VCO2) [35]. The gas analysis was continued until less than 5 % of REEm differences existed between two samples among the collected samples, and the mean value of the two samples was used for the analysis (coefficient of variation = 3.2 %).
For the prediction of REE, the Cunningham, Owen, Taguchi, ten Haaf and Weijs, and Kim equations were used in this study [16,20,28,30,34]. The selection of the equations was based on their components and on the database of the population included in their development. FFM-based equations developed from participants, involving athletes, were selected, and the Cunningham equation (1980) was also included, considering its high validity in athletes [29].
The IBM software, Statistical Packages for the Social Sciences (SPSS statistics version 26, IBM, Somers, NY, USA), was used for statistical analysis, with a significance level of p set at <0.05. The distribution of the collected data was checked using the Shapiro-Wilk test, and non-normally distributed data were analyzed using non-parametric tests. All data were expressed as means ± standard deviation (SD). To analyze the differences between REEm and REEp, paired t-tests were used, and the constant error (CE) and Cohen’s d effect size (ES) were calculated. The relationships between REEm and REEp were analyzed using Pearson’s correlation coefficient (r) and the coefficient of determination (R2). The errors in the REE-prediction equations were analyzed by calculating the standard error of the estimate (SEE) and root mean square error (RMSE). Additionally, the Bland-Altman method was used to determine the 95 % limits of agreement (LOA) between the REEm and REEp to analyze the accuracies of the prediction equations [36]. Linear regression analysis was used to analyze the proportional bias between REEm and REEp [37].
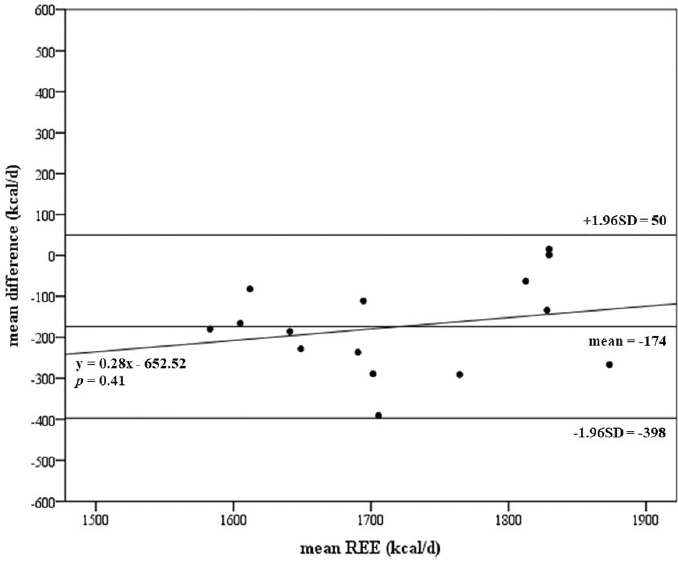
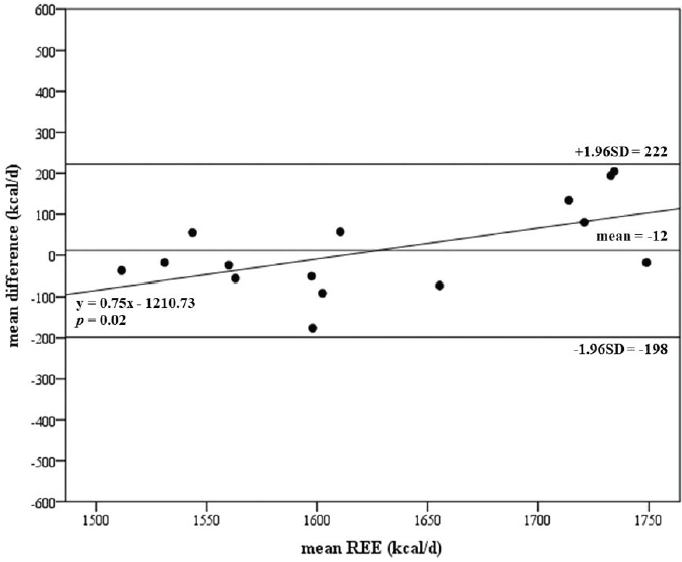
The descriptive characteristics of the participants are presented in Table 2. The differences between the REEm and REEp are presented in Table 3. REE p using the Cunningham and ten Haaf and Weijs equations were significantly different from REEm (REEm 1,634 ± 122 kcal/d vs. Cunningham 1,808 ± 99 kcal/d, p <0.001; vs. ten Haaf and Weijs 1,838 ± 103 kcal/d, p <0.001). However, the REE p using the Owen, Taguchi, and Kim equations were not significantly different from the REEm (Owen 1,589 ± 106 kcal/d, p <0.159; Taguchi 1,640 ± 124 kcal/d, p <0.852; Kim 1,622 ± 68 kcal/ d, p <0.670). The Taguchi and Kim equations had a low CE ± SD and very small (<0.2) Cohen’s d ES (Taguchi -6 ± 125, -0.05; Kim 12 ± 107, 0.11) than the Owen equation (45 ± 117, 0.38). The relationships between the REEm and the accuracy of the REE-prediction equations are presented in Table 4, and Figures 1 to 5 show the Bland-Altman plots for the REEm and REEp. All the equations showed a similar r, R2, p values, and 95 % LOA. The Kim equation showed the lowest SEE and RMSE (62 kcal/d and 104 kcal/ d, respectively), but it also showed a significantly positive proportional bias (0.75, p = 0.02). The Taguchi equation also showed a low RMSE (121 kcal/d) but no significant proportional bias (-0.02, p = 0.95).
This study aimed to compare the differences between the REEp, using different FFM-based REE-prediction equations, and the REEm in Korean male collegiate soccer players. The main finding of this study was that the Taguchi equation provided a better estimation of REE than other FFM-based REE-prediction equations in Korean male collegiate soccer players. The Cunningham and ten Haaf and Weijs equations provided a significant overestimation of the REE. The Owen equation showed a higher CE and ES than the Taguchi equation, and the Kim equation showed a positive proportional bias.
The body composition of the participants (height 175.1 ± 4.8 cm; weight 68.88 ± 5.48 kg; body fat 13.6 ± 2.5 %; and FFM 59.5 ± 4.5 kg) was similar to that in previous study on Korean male collegiate soccer players (height 177.1 ± 5.9 cm; weight 71.60 ± 6.26 kg; body fat 13.9 ± 3.4 %; and FFM 59.7 ± 7.4 kg) [38]. Kim et al. developed their prediction equation from 100 Korean athletic and non-athletic adolescents, including 30 male soccer players, with similar body composition to that of the participants in this study (height 176.9 ± 5.3 cm; weight 68.1 ± 5.3 kg; body fat 11.1 ± 2.2 %; and FFM 60.5 ± 4.5 kg) [30]. A previous study involving Japanese male athletes categorized the participants into three groups: small, medium, and large groups, according to their anthropometric characteristics [33]. The participants of the present study fall between the small (height 171.2 ± 5.9 cm; weight 67.1 ± 4.8 kg; body fat 12.9 ± 2.4 %; and FFM 58.4 ± 4.1 kg) and medium (height 174.8 ± 6.0 cm; weight 77.1 ± 2.9 kg; body fat 13.1 ± 3.5 %; and FFM 66.7 ± 1.9 kg) groups of the mentioned study. The metabolically active compartments of the FFM can be categorized as bone mass, adipose tissue, skeletal muscle, and residual mass, and a larger body size can change the contribution of these metabolically active tissues to the REE, resulting decrease in the REE/FFM ratio in untrained adults [39]. However, studies involving Japanese collegiate athletes have demonstrated that the contribution of organ tissues to REE remains constant regardless of the body size of the participants [21,33]. A longitudinal study involving American football players during a 1-year period of overfeeding and physical training demonstrated an increase in organ-tissue mass with a consistent proportion of organ-tissue mass in FFM, which can be explained by the adaptation of organ tissue to increased functional load [40]. The contribution of fat mass (FM) to REE prediction cannot be ignored in obese individuals and older healthy individuals; however, FM in non-obese individuals and athletes is relatively constant, and the contribution of FM to REE prediction is small [17,41,42]. Thus, the prediction of REE using the FFM-based equations in athletes can be recommended regardless of body size; however, it should take into account the effect of sport types and training practices that can affect the proportion of organ-tissues in body composition and REE prediction.
The REEp using the Cunningham and ten Haaf and Weijs equations were significantly overestimated (Table 1), and they showed a high RMSE (Table 2). However, previous studies have shown that the Cunningham equation predicted REE with high accuracy in both male and female athletes [28,32]. A recent study involving trained male athletes reported significantly underestimated REE using the Cunningham equation [43]. The measured REE and REE/FFM of male athletes in the previous studies were 1,868 ± 239 kcal/ d and 29.5 ± 2.5 kcal/kg FFM/d, 2,007 ± 206 kcal/d and 30.0 kcal/kg FFM/d, and 2,405 ± 290 kcal/d and 30.4 kcal/ kg FFM/d approximately, which were higher than the values obtained in this study (1,634 ± 122 kcal/d and 27.6 ± 2.1 kcal/kg FFM/d) [28,32,43]. The different REE measurement procedures and devices might have an influence on these under/ overestimations of REEm, and the effect of race/ethnicity on the REE could also explain these differences [44]. Furthermore, the Cunningham and ten Haaf and Weijs equations were both developed from Caucasian participants, and the contribution of FFM and the constants of the two equations were similar (Cunningham 22 × FFM + 500 and ten Haaf and Weijs 22.771 × FFM + 484.264). However, the Cunningham equation excluded athletes from the Harris and Benedict study, and ten Haaf and Weijs included only athletes [16,18,28].). The similar contribution of the FFM to the REE-prediction equations of these two studies might be a coincidence, considering the differences between the participants and measurement methods; however, it still demonstrates the importance of the FFM in the prediction of REE.
The REEp using the Owen equation was not significantly different from the REEm, but it showed a high CE ± SD and RMSE. The Owen equation was developed from a study involving 60 males and 44 females including lean, obese, and trained athletes with a variation of age, BW, and race/ethnicity [20]. To develop the Owen equation, data from relatively diverse populations were used, unlike the Taguchi and Kim equations; this could result in a higher rate of error during REE prediction [20,21,30]. The Taguchi and Kim equations showed a higher accuracy of REE prediction with non-significant differences and lower errors than the other FFM-based equations. However, the Kim equation showed a significantly positive proportional bias (0.75, p = 0.02); this implies the Kim equation may underestimate REE in participants with high REE and overestimate REE in participants with low REE. The Kim equation was developed from the data of 100 Korean adolescents, including athletes and non-athletes, and there were significant differences in body composition and the degree of correlation between FFM and REE in the participant groups; these might have affected the accuracy of REE prediction [30]. The Taguchi equation was developed using data obtained from 205 Japanese female athletes with various body sizes, but the ratio between REE and FFM was constant regardless of body size, an aspect which might have increased the accuracy of REE prediction in this study [21,34]. The generalized equations could be convenient for REE prediction in large population groups with various characteristics; however, the accuracy of the prediction can be significantly decreased in specific population groups such as athletes [23]. Thus, it is important to consider the characteristics of the participants when choosing the equation for REE prediction. Moreover, further studies are required to develop athlete-specific REE-prediction equations.
To the best of our knowledge, this study is the first to compare the differences between REEp, using FFM-based REE equations, and REEm in Korean collegiate athletes; however, there are several limitations. The number of participants was not sufficient to adequately analyze the validity of the equations and the measurement errors in REE and body composition might have affected the results. In addition, the energy deficiency of the participants was not considered, though it could have affected their metabolic rates [39].
In conclusion, the Taguchi equation provides the best REE prediction for Korean male collegiate soccer players. The Owen and Kim equations also provided fair estimations of REE in this study, but the narrow characteristics of the participants in this study might have increased the differences with the REEm. Therefore, it is recommended to consider the characteristics of the target population, especially athletic nature and race/ethnicity, for a precise REE prediction. Future studies should consider using a larger number of participants to analyze the validity of these equations.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank the participants, coaches, and staff of Yongin University for supporting this study. We sincerely appreciate Ms. Seungah Han for helping in the measurements and arrangement of the laboratory. In addition, we acknowledge Mizuki Kato and Okumura Koichiro for their assistance with the data collection. This research was supported by Waseda University Grants for Special Research Projects (“Tokutei Kadai”) in 2018.
Table 1.
REE prediction equations.
Table 2.
Descriptive characteristics of the participants.
| Total (n=15) | |
|---|---|
| Age (years) | 19.1 ± 0.8 |
| Height (cm) | 175.1 ± 4.8 |
| Weight (kg) | 68.88 ± 5.48 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 22.4 ± 1.1 |
| Body fat (%) | 13.6 ± 2.5 |
| Body fat (kg) | 9.4 ± 2.1 |
| FFM (kg) | 59.5 ± 4.5 |
Table 3.
Differences between measured and predicted REE.
Table 4.
Statistical analysis between measured and predicted REE.
REFERENCES
1. Mountjoy M, Sundgot-Borgen J, Burke L, Ackerman KE, Blauwet C, Constantini N, Lebrun C, Lundy B, Melin A, Meyer N, Sherman R, Tenforde AS, Torstveit MK, Budgett R. International Olympic Committee (IOC) consensus statement on relative energy deficiency in sport (RED-S): 2018 update. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab 2018;28:316-31.


2. Mountjoy M, Sundgot-Borgen J, Burke L, Carter S, Constantini N, Lebrun C, Meyer N, Sherman R, Steffen K, Budgett R, Ljungqvist A. The IOC consensus statement: beyond the female athlete triad--relative energy deficiency in sport (RED-S). Br J Sports Med 2014;48:491-7.


3. Koehler K, Achtzehn S, Braun H, Mester J, Schaenzer W. Comparison of self-reported energy availability and metabolic hormones to assess adequacy of dietary energy intake in young elite athletes. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab 2013;38:725-33.


4. Moss SL, Randell RK, Burgess D, Ridley S, ÓCairealláin C, Allison R, Rollo I. Assessment of energy availability and associated risk factors in professional female soccer players. Eur J Sport Sci 2021;21:861-70.


5. Nattiv A, De Souza MJ, Koltun KJ, Misra M, Kussman A, Williams NI, Barrack MT, Kraus E, Joy E, Fredericson M. The male athlete triad-a consensus statement from the female and male athlete triad coalition part 1: definition and scientific basis. Clin J Sport Med 2021;31:345-53.

6. Reed JL, De Souza MJ, Williams NI. Changes in energy availability across the season in division I female soccer players. J Sports Sci 2013;31:314-24.


7. Areta JL, Taylor HL, Koehler K. Low energy availability: history, definition and evidence of its endocrine, metabolic and physiological effects in prospective studies in females and males. Eur J Appl Physiol 2021;121:1-21.




8. Koehler K, De Souza MJ, Williams NI. Less-than-expected weight loss in normal-weight women undergoing caloric restriction and exercise is accompanied by preservation of fat-free mass and metabolic adaptations. Eur J Clin Nutr 2017;71:365-71.



9. Stenqvist TB, Torstveit MK, Faber J, Melin AK. Impact of a 4-week intensified endurance training intervention on markers of relative energy deficiency in sport (RED-S) and performance among well-trained male cyclists. Front Endocrinol 2020;11:512365.



10. De Souza MJ, Hontscharuk R, Olmsted M, Kerr G, Williams NI. Drive for thinness score is a proxy indicator of energy deficiency in exercising women. Appetite 2007;48:359-67.


11. Sterringer T, Larson-Meyer DE. RMR ratio as a surrogate marker for low energy availability. Curr Nutr Rep 2022;11:263-72.



12. De Souza MJ, Koltun KJ, Strock NCA, Williams NI. Rethinking the concept of an energy availability threshold and its role in the female athlete triad. Curr Opin Physiol 2019;10:35-42.

13. Strock NC, Koltun KJ, Southmayd EA, Williams NI, De Souza MJ. Indices of resting metabolic rate accurately reflect energy deficiency in exercising women. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab 2020;30:14-24.


14. Ferrannini E. The theoretical bases of indirect calorimetry: a review. Metabolism 1988;37:287-301.


16. Cunningham JJ. A reanalysis of the factors influencing basal metabolic rate in normal adults. Am J Clin Nutr 1980;33:2372-4.


17. Cunningham JJ. Body composition as a determinant of energy expenditure: a synthetic review and a proposed general prediction equation. Am J Clin Nutr 1991;54:963-9.


18. Harris JA, Benedict FG. A biometric study of basal metabolism in man. Carnegie Institution of Washington. 1919.
19. Mifflin MD, St Jeor ST, Hill LA, Scott BJ, Daugherty SA, Koh YO. A new predictive equation for resting energy expenditure in healthy individuals. Am J Clin Nutr 1990;51:241-7.


21. Taguchi M, Ishikawa-Takata K, Tatsuta W, Katsuragi C, Usui C, Sakamoto S, Higuchi M. Resting energy expenditure can be assessed by fat-free mass in female athletes regardless of body size. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol 2011;57:22-9.


22. Schofield KL, Thorpe H, Sims ST. Resting metabolic rate prediction equations and the validity to assess energy deficiency in the athlete population. Exp Physiol 2019;104:469-75.



23. Frankenfield D, Roth-Yousey L, Compher C. Comparison of predictive equations for resting metabolic rate in healthy nonobese and obese adults: a systematic review. J Am Diet Assoc 2005;105:775-89.


24. Gannon B, DiPietro L, Poehlman E. Do African Americans have lower energy expenditure than Caucasians? Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 2000;24:4-13.



25. Lee G-H, Kim M-H, Kim E-K. Accuracy of predictive equations for resting metabolic rate in Korean college students. Korean J Community Nutr 2009;14:462-73.
26. Miyake R, Tanaka S, Ohkawara K, Ishikawa-Takata K, Hikihara Y, Taguri E, Kayashita J, Tabata I. Validity of predictive equations for basal metabolic rate in Japanese adults. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol 2011;57:224-32.


27. Xue J, Li S, Zhang Y, Hong P. Accuracy of predictive resting-metabolic-rate equations in Chinese mainland adults. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2019;16:2747.



28. ten Haaf T, Weijs PJ. Resting energy expenditure prediction in recreational athletes of 18-35 years: confirmation of Cunningham equation and an improved weight-based alternative. PLoS One 2014;9:e108460.



29. Tinsley GM, Graybeal AJ, Moore ML. Resting metabolic rate in muscular physique athletes: validity of existing methods and development of new prediction equations. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab 2019;44:397-406.


30. Kim JH, Kim MH, Kim GS, Park JS, Kim EK. Accuracy of predictive equations for resting metabolic rate in Korean athletic and non-athletic adolescents. Nutr Res Pract 2015;9:370-8.



31. Mackay KJ, Schofield KL, Sims ST, McQuillan JA, Driller MW. The validity of resting metabolic rate-prediction equations and reliability of measured RMR in female athletes. Int J Exerc Sci 2019;12:886-97.


32. Thompson J, Manore MM. Predicted and measured resting metabolic rate of male and female endurance athletes. J Am Diet Assoc 1996;96:30-4.


33. Oshima S, Miyauchi S, Kawano H, Ishijima T, Asaka M, Taguchi M, Torii S, Higuchi M. Fat-free mass can be utilized to assess resting energy expenditure for male athletes of different body size. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol 2011;57:394-400.


34. Taguchi M, Ishikawa-Takata K, Ouchi S, Higuchi M. Validity of prediction equation of basal metabolic rate based on fat-free mass in Japanese female athletes. Jpn J Phys Fit Sports Med 2011;60:423-32.

35. Weir JDB. New methods for calculating metabolic rate with special reference to protein metabolism. J Physiol 1949;109:1-9.



36. Bland JM, Altman DG. Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet 1986;1:307-10.


37. Tinsley GM. Proportional bias between dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry and bioelectrical impedance analysis varies based on sex in active adults consuming high-and low-carbohydrate diets. Nutr Res 2017;42:85-100.


38. Jeong J-H, Kim S-E, Kim H-J, Park J-J, Lee S-H. A study on the compare analyzed of body composition, physical strength, and anaerobic power of male middle, high school, and college soccer players. KJS 2019;17:1111-21.
39. Heymsfield SB, Gallagher D, Kotler DP, Wang Z, Allison DB, Heshka S. Body-size dependence of resting energy expenditure can be attributed to nonenergetic homogeneity of fat-free mass. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2002;282:E132-8.


40. Miyauchi S, Oshima S, Asaka M, Kawano H, Torii S, Higuchi M. Organ size increases with weight gain in power-trained athletes. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab 2013;23:617-23.


41. Oshima S, Miyauchi S, ASAkA M, Kawano H, Taguchi M, Torii S, Higuchi M. Relative contribution of organs other than brain to resting energy expenditure is consistent among male power athletes. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol 2013;59:224-31.


42. Taguchi M, Tatsuta W, Higuchi M. Resting energy expenditure of female athletes in different types of sport. Jpn J Nutr Di 2010;68:289-97.

-
METRICS

-
- 1 Crossref
- Scopus
- 2,752 View
- 38 Download
- Related articles in Phys Act Nutr