|
 |
- Search
| Phys Act Nutr > Volume 18(2); 2014 > Article |
|
Abstract
[Purpose]
The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of treadmill exercise on inflammatory response in streptozotocin (STZ)-induced animal model of Alzheimer’s disease (AD).
[Methods]
To induce the animal model of AD, Sprague-Dawley rats were injected into intracerebroventricular (ICV) injection with 1.5 mg/kg of STZ. Rats were divided into three groups as Sham-con group (n = 7), STZ-con group (n = 7) and STZ-exe group (n = 7). Exercise group ran on the treadmill for 30 min/day, 5 days/week during 6 weeks.
[Results]
The results of this study were as follows: First, STZ-exe group was improved on cognitive function when compared to STZ-con group in water maze test. Second, STZ-exe group help reduce the expression level of amyloid-beta (Aβ). In addition, Toll-like receptors-4 (TLR4), Nuclear factor-kB (NF-kB), Tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and Interleukin-1α (IL-1α) level of STZ-exe group was significantly decreased when compared to STZ-con group.
Along with the increase of elderly population worldwide, the incidence of diverse neurodegenerative diseases appears as a serious problem in society. Especially, one of the neurodegenerative diseases, dementia, arises as early as over thirty years old or commonly occurs in the elderly population, and is characterized by agnosia, apraxia, and aphasia [1]. Currently, in Korea due to rapid aging, patients with dementia among the elderly over 65 years old have reached 9.2%, 560 thousand, and among these, dementia of sporadic Alzheimer’s type known as senile dementia accounts for 75% [2].
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) causes memory and multiple cognitive impairments and neurological dysfunction. Extracellular senile plaque composed of amyloid-beta (Aβ) causing toxicity in the brain and deposition of neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs) due to hyperphosphorylated tau protein within the cell are reported as major pathologic causes of nerve cell death [3]. Additionally, in the metabolic aspect, decrease of glucose utilization ability was observed in the brains of Alzheimer patients, and it is reported to be associated with cognitive impairment [4]. Interestingly, insulin produced in the β-cells of the pancreas moves to the brain by the cerebrospinal fluid, and functions physiologically or biochemically on organs around the brain, and insulin signaling impairment in the brain plays a major role in forming nerve fibers and plaque which are main lesions of AD [5-9]. Therefore, it seems that insulin signaling impairment in the brain plays a major role in forming nerve fibers and plaque which are main lesions of AD.
In fact, it is proposed that insulin signaling impairment in the brain decreases activation of insulin-mediated phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3-K)/Akt signaling, while results in excessive activation of glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK-3β) which hyperphosphorylates tau protein and consequently forms nerve fibers or accumulates Aβ forming senile plaque [9]. Moreover, insulin signaling impairment lowers glucose metabolism in the brain by inducing a decrease of expression of glucose transporter-1 (GLUT-1) and glucose transporter-3 (GLUT-3) protein. Recently, it is suggested that the decrease of glucose metabolism in the brain reduces the level of UDP-GlcNAc through hexosamine biosynthetic pathway (HBP), which promotes hyperphosphorylation of tau by decreasing tau O-GlcNAcylation [9]. As a result, insulin signaling impairment in the brain causes abnormalities of nerve functions and reduces cognitive abilities. In particular, it is revealed that one of the major lesions of AD, Aβ deposition, causes topical inflammation in a short- term while damages or eradicates nerve cells by accelerating inflammation in chronic conditions [10-13]. It is reported that the level of inflammatory cytokines increases markedly in the brains of Alzheimer patients and experimental animal models [14-17].
Since induction of Inflammation due to Aβ deposition is an almost identical result among researchers, it is important to develop methods that can prevent or reduce it as well as persistent research is required to investigate a mechanism for associations between Aβ deposition and induction of inflammation.
Recently, to establish prevention or treatment strategies for AD, various dementia related experimental animals have been actively developed and utilized. Among the dementia related animals, streptozotocin (STZ) injected mice into their intracerebroventriculars (ICV) are widely used as an experimental animal model of sporadic AD. In case of streptozotocin (STZ) injected mice into their intracerebroventriculars (ICV), it is revealed that impairment of the insulin receptor and disability in glucose metabolism were induced [18-22], and Aβ was significantly accumulated, which are the same symptoms with those of Alzheimer patients [4,23-25].
From the past and up to the present, in order to reduce the incidence of AD, neuroscientists have attempted a lot of efforts on preventing or delaying AD by reducing Aβ deposition using diverse methods including drugs such as tacrine, donepezil, rivastigmine and galantamine, antioxidants (turmeric, catechin, and phyto chemicals), omega-3 fatty acids, immunity, and cognitive training. However, the effects were reported as temporary or negative, while recently physical activity became to have more attention as an alternative preventing or delaying AD economically.
Looking at previous research related to associations between physical activity and AD as a result of regular exercise of animal models of AD, along with a decrease of Aβ, the level of cytokines lowered while cognitive function markedly improved [26-32]. And Toll-like receptors (TLRs), Interleukin-6 (IL-6) and Tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) are suggested as major indicators related to immune and inflammatory responses by exercise [33-34]. TLRs are the type I transmembrane signaling molecules and mainly expressed in the cells in charge of the innate immune system and play a role of regulating inflammation by transmitting signals causing immune responses. Nuclear factor-kB (NF-kB) exists in an inactive state combining with the inhibitor kB(IkB) suppressing NF-kb activation, but as IkB is phosphorylated through TLR4 signaling mechanism, it is activated after separated from NF-kB and moves to nuclei and causes inflammatory response by making inflammatory cytokine genes such as TNF-α, IL-1, and IL-6 expressed [35,36]. As a tumor necrosis factor, TNF-α is a typical cytokine inducing immune and inflammatory responses by causing necrosis. IL-1α is a typical inflammatory cytokine involved in all signaling pathways [37,38]. However, currently there is not enough research analyzing the effect of physical activity on inflammatory response induced by AD. Therefore, this study intends to analyze the effect of treadmill exercise on changes of TLR4, NF-κB, TNF-α, and IL-1α playing a central role in the signaling pathways of inflammatory response targeting the animal model of streptozotocin (STZ)-induced sporadic AD.
The animals used in this experiment were 20-week-old Sprague-Dawley rats (Samtako, Kyunggi-do, Korea) and raised in the same environment with the K university experimental animal room maintaining constant temperature (22 ± 2) and humidity (50%) in a photoperiod cycle of 12h:12h (day and night). During the experiment, Purina rat diet - 5057 manufactured according to AIN-76A diet for experimental animals presented at the American Nutrition Association was provided, and feeds and drinks were supplied without a limit. Groups were divided into Sham-control (Sham-con: n = 7), Streptozotocin-control (STZ-con: n = 7), and Streptozotocin-exercise (STZ-exe: n = 7).
In this experiment, to induce memory impaired rats, brain surgery was conducted. First, rats were anesthetized by intraperitoneal injection with 50 mg/kg of 1:1 mixture of Zoletil50® (Virbac Laboratories, Carros, France) and Rompun (Bayer Korea Ltd., Korea). Referring to the anatomical chart [39], the head of the rat was fixed in the stereotaxic frame, and streptozotocin (Sigma, USA) was injected into both intracerebroventriculars (ICVs) in the following way. From the surface of the skull, based on the bregma the point located 1.5 mm right and 0.8 mm posterior was drilled by a small drill with a diameter of 0.5 mm. And then a microinjector (10 μl, 26G, Hamilton. USA) was needled into the depth of 3.6 mm, and after diluting STZ with saline to 1.5 mg per weight, 10 μl of diluted solution was injected into the intracerebroventricular (ICV) [18,40]. After surgery, the incision site was sutured and sterilized. The animals were kept in a warm place and returned to the breeding box after recovery. For the Sham-con group, the same procedure was performed but only saline was injected.
For the experiment, the rat model of ICV-STZ-induced memory impairment was used, and the experiment was composed of three steps with a gradually increased speed. The rats received pre-adaptation training using the treadmill for experimental animals (Rodent, Treadmill, Dae-myung Scienific Co, Ltd, Korea) for one week fixing the slope at 0%. The strength of the pre-adaptation training was 2m/min for the first 5 minutes, 5m/min for the next 5 minutes, and 8m/min for the last 20 minutes. After the pre-adaptation training, based on the medium strength exercise program suggested by Kim et al. [41] and study results of Lee et al. [42], an exercise program was conducted 5 days per week for 6 weeks. The strength of the exercise was 8m/min for the first 5 minutes, 11m/min for the next 5 minutes, and 14m/min for the last 20 minutes.
Morris water maze test was conducted to examine the change in cognitive ability of the rat model of ICV-STZ-induced memory impairment. For the water maze test, in the water tank with a diameter of 100cm and a height of 40cm filled with 30 cm water in height (22℃ ± 2℃), a circular platform with a diameter of 15cm was submerged 3cm below the surface of water, and milk powder was dissolved in the water invisibly. After 6 weeks of treadmill running, the experimental animals’ escape latency, escape distance and escape pattern were measured and analyzed using a computer program, SMART 3.0 (Panlab, Spain), installed on the ceiling right above the water tank.
The water maze test was carried out for five days. Rats were trained everyday to start from the same location and reach the target placed in the same location three times each. On the last sixth day, after removing the circular platform, rats started to swim at the same starting place and reached the circular platform for 60 seconds a total of three times, and the records were used for analysis.
After performing 6 weeks of exercise and behavioral test, rats were anesthetized by intraperitoneal injection with 50 mg/kg of Zoletil50® (Virbac Laboratories, Carros, France) and Rompun (Bayer Korea Ltd., Korea). And then brain tissue was extracted and stored frozen at -80℃ until the analysis.
After 24 hours of the behavioral test, the experimental animals were anesthetized by intraperitoneal injection with Zoletil50® (Virbac Laboratoies, Carros, France) and Rompun (Bayer Korea Ltd., Korea). After opening the chest cavity, through the left ventricle, 50mM of phosphate buffered saline was injected, and then 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA) fixatives dissolved in 100 mM phosphate buffer was flew through. After perfusion fixation, brain was extracted, and after keeping the brain in fixatives at 4℃ for 12 hours, fixation was conducted. The fixed brain tissue was immersed in the 30% sucrose solution for two to five days, and then using cryostat (American Optica, USA), 40 μm thick serial coronal section was made.
10% separating gel (3DW, 30% acrylamide: bisacrylamide, 1.5 M tris pH 8.8, 10% SDS, TEMED, 10% Ammonium persulfate) and 5% stacking gel (3DW, 30% acrylamide: bisacrylamide, 1 M tris pH 6.8, 10% SDS, TEMED, 10% Ammonium persulfate) were utilized. After mixing centrifuged supernatant liquid (14,000 rpm, 30 min) with 2X Sample loading buffer (60 mM tris pH6.8, 25% glycerol, 2% SDS, 14.4 mM 2-mercaptoethanol, 0.1% Bromophenol blue) at 1:1 ratio, it was boiled at 100℃ for 10 minutes to denature protein. And then it was cooled in ice for 10 minutes and centrifuged again (14,000 rpm, 10 min). Along with the standard marker (pagerular prestained protein Ladder #SM0671-Fermentas), each sample was added to the stacking gel well prepared in the mini-Protein Ⅱ dual-slab apparatus (Bio-Rad, CA, USA) so the total amount of proteins was to be 30 μg. Electrophoresis was performed with 80 volt for about 120 minutes until the samples were touched to the bottom.
After activating the polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) membrane by soaking it in MeOH and washing it with transfer buffer (190 mM glycine, 50 mM Tris-base, 0.05% SDS, 20% methanol) three times, whatman 3M paper soaked by transfer buffer was overlaid sequentially and installed in the mini trans-bolt cell (Bio-Rad, CA, USA). Power was turned on with 45 volt for 120 minutes. After transferring, the membrane was placed on the rocker platform for an hour for blocking with 3% skim milk solution (in TBS-T: 10 mM tris-base pH 8.0, 150 mM NaCl, 0.05% Tween-20). Primary antibody was diluted with the blocking (3% skim milk) solution at 1:1000 and shaken for 90 minutes. After then, it was washed with TBS-T solution 3 times for 10 minutes and 2 times for 5 minutes. The secondary antibody (horseradish peroxidase-conjugated goat anti-rabbit 65-6120, ZYMED, CA, USA; horseradish peroxidase-conjugated rabbit anti-goat 81-1620, ZYMED, CA, USA; horseradish peroxidase-conjugated goat anti-mouse sc-2005, Santa Cruz, CA, USA) was diluted with blocking solution at 1:5000 and shaken for 90 minute. After then it was washed with TBS-T solution 3 times for 10 minutes and 2 times for 5 minutes. At the last step, the membrane obtained by putting the membrane in the Western Blotting Luminol Reagent (WBLR) solution for one minute for color fixation was scanned using the image analysis system (Molecular Imager Chemi Doc XRS System, Bio-Rad, USA), and the amounts of proteins were calculated using the Quantity One 1-D Analysis Software (Bio-Rad, USA).
For the immunohistochemical method, using the free- floating method, from each group six sheets were selected and washed three times for 5 minutes each. To remove peroxidase, they were shaken in 50% ethyl alcohol for 30 minutes, and then washed in 0.01 M PBS 3 times for 5 minutes each. And each tissue was put in the beaker filled with 0.01 M sodium citrate and incubated for 8 minutes in the boiling water (100℃). Blocking was performed for 40 minutes using 10% normal donkey serum (2309032, millipore, USA). After blocking, primary antibody beta-amyloid (39320, Covance Inc, USA) was kept at 4℃ for 12 hours overnight. After overnight, it was washed in 0.01 M PBS three times for 5 minutes each and reacted with the horseradish peroxidase-conjugated goat anti-mouse (sc-2005, Santa Cruz, CA, USA) at the room temperature for an hour. It was washed again in the 50 Mm PBS three times for 5 minutes each, and RT incubation was carried out with vectastain-Elite ABC kit (PK-6200, Vector Laboratories, USA) solution for 30 minutes. It was washed in 0.01 M PBS three times for 5 minutes each, and DAB (3,3‘-diaminobenzidine tetrahydrochloride) was diluted to 0.02% in 0.05 M tris-buffer (pH 7.6) using DAB Peroxidase Substrate Kit (SK-4100, Vector Laboratories, USA), and was color-fixed by adding 0.02% hydrogen peroxide for 5 minutes. The tissue completing color fixation was washed with 0.01 M PBS three times. After attached in the gelatin-coated slide, it was completely dried in the RT and dehydrated in ethyl alcohol having the concentration increased by 80%, 90%, and 100%. After completion of the dehydration process, it became transparent by 80%, 90%, and 100% xylene and sealed using permount.
For data analysis, using SPSS/PC 18.0 statistical package, descriptive statistics (mean ± SD) were calculated, and one-way ANOVA was performed for comparison between groups. When there was a statistically significant difference between groups, post-hoc tests were conducted. The significance level was set to α = 0.05.
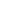
Targeting animals of STZ-induced Alzheimer’s disease by intracerebroventricular (ICV) injection, the effect of 6-week endurance exercise on the memory change was investigated. The results were as follows <Fig. 1A, B>. First, in the swimming time, there was a difference between groups First, in the escape latency, there was a difference between groups (F(2, 20) = 104.98, P < 0.001), and according to the post-hoc test, compared to the STZ-con group escape latency the Sham-con group and STZ-exe group was statistically significantly short (P < 0.001). In the escape distance, there was a difference between groups (F(2, 20) = 30.933, P < 0.001), and according to the post-hoc test, compared to the STZ-con group, the escape distance of Sham-con group and STZ-exe group was statistically significantly short (P < 0.001).
Targeting animals of STZ-induced AD by intracerebroventricular (ICV) injection, the effect of 6-week endurance exercise on the Aβ expression change was analyzed using protein analysis and immunohistochemical staining method (DAB Method) <Fig. 2>. First, in the level of protein <Fig. 2-A>, there was a difference between groups (F(2,11) = 889.379, P < 0.001), and according to the post-hoc test, compared to the STZ-con group, the level of Aβ expression significantly decreased in the Sham-con group and the STZ-exe group (p = 0.001; p < 0.001). Additionally, in the immunohistochemical staining <Fig. 2-B>, Aβ deposition was higher in the STZ-con group and the STZ-exe group than in the Sham-con group. Especially, in the cerebral cortex of the STZ-con group, Aβ deposition appeared in a broader range than in the cerebral cortex of the STZ-exe group.
Targeting animals of STZ-induced AD by intracerebroventricular (ICV) injection, the effect of 6-week endurance exercise on changes of TLR4 and NF-kB was analyzed <Fig. 3>. First, for TLR4 <Fig. 3-B>, there was a difference between groups (F(2,11) = 9.056, P < 0.01), and according to the post-hoc test, compared to the STZ-con group, the level of TLR4 expression significantly decreased in the Sham-con group and the STZ-exe group (p = 0.002; p = 0.023). Additionally, for NF-kB <Fig. 3-C>, there was a difference between groups (F(2,11) = 192.743, P < 0.001), and according to the post-hoc test, compared to the STZ-con group, the level of NF-kB expression statistically significantly decreased in the Sham-con group and STZ-exe group respectively (p < 0.001).
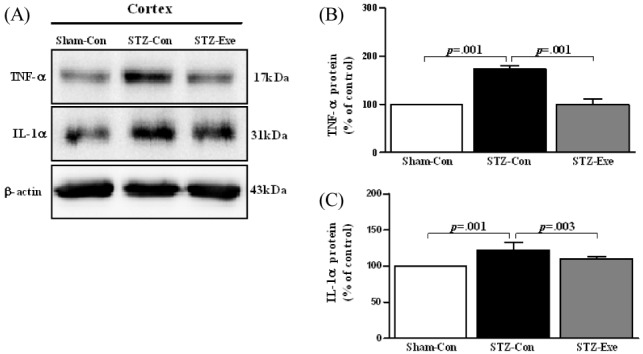
Targeting animals of STZ-induced AD by intracerebroventricular (ICV) injection, the effect of 6-week endurance exercise on changes of TNF-α and IL-1α Expression was analyzed <Fig. 4>. First, for TNF-α <Fig. 4-B>, there was a difference between groups (F(2,11) =136.144, P <0.001), and according to the post-hoc test, compared to the STZ-con group, the level of TNF-α expression significantly decreased in the Sham-con group and the STZ-exe group (p < 0.001). Additionally, for IL-1α <Fig. 4-C>, there was a difference between groups (F(2, 11) = 11.864, P = 0.003), and according to the post-hoc test, compared to the STZ-con, the level of IL-1α expression significantly decreased in the Sham-con group and the STZ-exe group (p < 0.001, p = 0.003).
Generally, injection of STZ into intracerebroventricular (ICV) impairs cognitive function by occurring dysfunction of glucose metabolism in the brain as well as suppresses activation of enzymes essential to insulin resistance and corresponding processes by selectively reducing the autophosphorylation process of the insulin receptor [19,21]. In addition, it is reported that injection of STZ into intracerebroventricular (ICV) reveals the same symptoms with those of patients with AD such as lowered insulin resistance and cognitive function occurring pathologically due to significant deposition of Aβ [23-25]. Therefore, this study analyzed the effect of treadmill exercise on inflammation response occurring in the brain of the animal model of AD with insulin signaling impairment by STZ injection into intracerebroventricular (ICV).
First, the result of the water maze test to examine the effect of treadmill exercise on cognitive function showed that compared to the STZ-con, cognitive function of the STZ-exe improved, which is consistent with the study result of Rodrigues et al. [43] that treadmill exercise improved cognitive function targeting the animal model of ICV-STZ-induced Alzheimer’ s disease. Moreover it coincides with previous study results that treadmill exercise improved cognitive function targeting animal models of TG2576, APPsw, Tau23 or PS2m-induced AD [26-32]. Improvement of cognitive function by regular exercise can be explained as caused by interactions of reduced oxidative stress and inflammatory response due to the reduction of the main lesion of AD, Aβ, nerve cell death suppression due to the efficiency of insulin and glucose metabolism and increase of nerve growth factor, brain plasticity and neurogenesis, etc.
On the other hand, Aβ deposition due to one of the causes occurring AD, insulin signaling impairment, seems to occur nerve cell death by inducing increase of inflammatory cytokines (TLR4, NF-kB, TNF-α, Cox-2, IL-1α, IL-1β). Park et al. [44] proposed that Aβ deposition in the brain (cerebral cortex or hippocampus) kills brain cells by causing inflammatory response, and Leem et al. [31] also suggested that nerve inflammatory response (TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, COX-2, and iNOS) is high in AD caused by hyperphosphorylation of tau protein.
In this study, Aβ deposition in the animal model of ICV-STZ-induced AD was considerably high, which is consistent with previous studies of Salkovic-Petrisic et al. [45] and Jung et al. [25] using the same animal model of ICV-STZ-induced AD. In addition, Aβ deposition pattern was the same as that of TG2576, APPsw, Tau23 or PS2m-induced AD animal models [26-32], which implies that animal model of AD has advantages.
Like this, Aβ deposition in the brain increases cytotoxicity and activates inflammatory response by abnormal regulation of Aβ generation and removal due to mutation of Alzheimer disease related genes and insulin signaling impairment, and acceleration of oxidative stress [10,46,47,48]. Jin et al. [49] reported that TLR-4 signaling mechanism activating NF-kB, an important nuclear transcription factor starting gene transcription related to immune and inflammatory response is activated as Aβ accumulates.
This study also showed that in the STZ-con group, protein expression of TLR4, NF-kB,TNF-α, and IL-1α was markedly high as well as the level of Aβ deposition was high, which coincides with the results of previous studies that activation of NF-kB by TLR4 caused by Aβ deposition activates inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-1α [31,32, 49-51]. On the other hand, it is known that physical activities or exercises inhibit Aβ generation. In this study as a result of long-term treadmill exercise targeting the animal model of ICV-STZ-induced AD, it was verified that Aβ deposition in the brain significantly decreases, which can be explained as a mechanism suggested by Salkovic-Petrisic and Hoyer [8]. Namely, long-term regular exercise seems to decrease activation of β or γ-secretase directly involved in Aβ generation by improving insulin-mediated insulin signaling impairment (PI3-K/Akt signaling activation increase and GSK-3β activation decrease). This result is also consistent with the study results of Um et al. [30] and Kang et al. [32].
Moreover, the reduction of Aβ seems to be directly related to the decrease of nerve inflammation response. In this study, compared to the STZ-con group, protein expression of TLR4, NF-kB, TNF-α and IL-1α was found to be significantly decreased in the STZ-exe group. As presented earlier, the change coincides with previous study results that long-term treadmill exercise decreases activation of NF-kB by TLR4 by decreasing Aβ deposition, and further activation of inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-1α was reduced [30-32,50-53].
Consequently, it was verified that insulin signaling impairment in the brain increases Aβ deposition, activates NF-kB by TLR4, and promotes inflammation by activating inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-1α. Meanwhile, long-term treadmill exercise seems to decrease Aβ generation by decreasing activation of β or γ-secretase through improvement of insulin-mediated insulin signaling impairment (PI3-K/Akt signaling activation increase and GSK-3β activation decrease). The decrease of Aβ directly reduces activation of NF-kB by TLR4, and further reduces inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-1α.
However, more specific future study is required because there are not many studies investigating effects of physical activities or exercises on neurodegenerative disease, AD, and inflammatory response.
This study analyzed the effect of treadmill exercise on inflammatory response in the brain of the animal model of ICV-STZ-induced AD. The results reveals that long-term treadmill exercise decreases the major lesion of AD, Aβ deposition, along with improvement of cognitive function, and the decrease of Aβ reduces activation of NF-kB by TLR4 controlling inflammatory cytokines and further reduces activation of inflammatory cytokine such as TNF-α and IL-1α. Therefore, long-term treadmill exercise is shown to be able to play a role as an alternative to prevent and treat AD by improving inflammatory response through reduction of the major lesion of AD, Aβ.
REFERENCES
1. Caselli RJ, Beach TG, Yaari R, Reiman EM. Alzheimer's disease a century later. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 2006;67(11):1784-800. PMID: 17196061.


2. Ministry of Health & Welfare 2009.
3. Selkoe DJ. Alzheimer's disease: genes, proteins, and therapy. Physiological Reviews 2001;81(2):741-766. PMID: 11274343.

4. Hoyer S. Brain glucose and energy metabolism during normal aging. Aging(milano) 1990;2(3):245-258. PMID: 1982730.


5. Banks WA. The source of cerebral insulin. European Journal of Pharmacology 2004;490(1-3):5-12. PMID: 15094069.


6. Burns JM, Donnelly JE, Anderson HS, Mayo MS, Spencer-Gardner L, Thomas G, Cronk BB, Haddad Z, Klima D, Hansen D, Brooks WM. Peripheral insulin and brain structure in early Alzheimer disease. Neurology 2007;69(11):1094-104. PMID: 17846409.

7. Erol A. An integrated and unifying hypothesis for the metabolic basis of sporadic Alzheimer's disease. Journal of Alzheimer's Disease 2008;13(3):241-53.


8. Salkovic-Petrisic M, Hoyer S. Central insulin resistance as a trigger for sporadic Alzheimer-like pathology: an experimental approach. Journal of Neural Transmission 2007 (72):217-33. Diabetes. 2007;55(3):760-7. PMID: 17982898.

9. Correia SC, Santos RX, Perry G, Zhu X, Moreira PI, Smith MA. Insulin-resistant brain state: the culprit in sporadic Alzheimer's disease? Ageing Res Rev 2011;10(2):264-273. PMID: 21262392.



10. Akiyama H, Barger S, Barnum S, Bradt B, Bauer J, Cole GM, Cooper NR, Eikelenboom P, Emmerling M, Fiebich BL, Finch CE, Frautschy S, Griffin WS, Hampel H, Hull M, Landreth G, Lue L, Mrak R, Mackenzie IR, McGeer PL, O'Banion MK, Pachter J, Pasinetti G, Plata-Salaman C, Rogers J, Rydel R, Shen Y, Streit W, Strohmeyer R, Tooyoma I, Van Muiswinkel FL, Veerhuis R, Walker D, Webster S, Wegrzyniak B, Wenk G, Wyss-Coray T. Inflammation and Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiology of Aging 2000;21(3):383-421. PMID: 10858586.



11. McGeer PL, McGeer EG. Inflammation, autotoxicity and Alzheimer disease. Neurobiology of Aging 2001;22(6):799-809. PMID: 11754986.


12. McGeer PL, McGeer EG. Autotoxicity and Alzheimer disease. Archives of Neurology 2000;57(6):789-90. PMID: 10867774.


13. Patel NS, Paris D, Mathura V, Quadros AN, Crawford FC, Mullan MJ. Inflammatory cytokine levels correlate with amyloid load in transgenic mouse models of Alzheimer's disease. J Neuroinflammation 2005;2(1):9PMID: 15762998.



14. Mehlhorn G, Hollborn M, Schliebs R. Induction of cytokines in glial cells surrounding cortical beta-amyloid plaques in transgenic Tg2576 mice with Alzheimer pathology. Int J Dev Neurosci 2000;18(4):23-31.
15. Apelt J, Schliebs R. Beta-amyloid-induced glial expression of both pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines in cerebral cortex of aged transgenic Tg2576 mice with Alzheimer plaque pathology. Brain Res 2001;891:21-30. PMID: 11245811.

16. Abbas N, Bednar I, Mix E, Marie S, Paterson D, Ljungberg A, Morris C, Winblad B, Nordberg A, Zhu J. Up-regulation of the inflammatory cytokines IFNgamma and IL-12 and down-regulation of IL-4 in cerebral cortex regions of APP(SWE) transgenic mice. J Neuroimmunol 2002;126:50-7. PMID: 12020956.


17. Meraz-Ríos MA, Toral-Rios D, Franco-Bocanegra D, Villeda-Hernández J, Campos-Peña V. Inflammatory process in Alzheimer's Disease. Front Integr Neurosci 2013;7:59PMID: 23964211.


18. Ishrat T, Khan MB, Hoda MN, Yousuf S, Ahmad M, Ansari MA, Ahmad AS, Islam F. Coenzyme Q10 modulates cognitive impairment against intracerebroventricular injection of streptozotocin in rats. Behavioural Brain Research 2006;171(1):9-16. PMID: 16621054.


19. Romanovsky D, Cruz NF, Dienel GA, Dobretsov M. Mechanicalhyperalgesia correlates with insulin deficiency in normoglycemicstreptozotocintreatedrats. Neurobiol Dis 2006;24:384-394. PMID: 16935517.


20. Duelli R, Schrock H, Kuschinsky W, Hoyer S. Intracerebroventricular injection of streptozotocin induces discrete local changes in cerebral glucose utilization in rats. International Journal of Developmental Neuroscience 1994;12:737-743. PMID: 7747600.

21. Grünblatt E, Salkovic-Petrisic M, Osmanovic J, Riederer P, Hoyer S. Brain insulin system dysfunction in streptozotocinintracerebroventricularly treated rats generates hyperphosphorylated tau protein. J Neurochem 2007;101(3):757-70. PMID: 17448147.


22. Lannert H, Hoyer S. Intracerebroventricular administration of streptozotocin causes long-term diminutions in learning and memory abilities and in cerebral energy metabolism in adult rats. Behavioral Neuroscience 1998;112:1199-1208. PMID: 9829797.



23. Lester-Coll N, Rivera EJ, Soscia SJ, Doiron K, Wands JR, de la Monte SM. Intracerebralstreptozotocin model of type 3 diabetes: relevance to sporadic Alzheimer's disease. Journal of Alzheimer's Disease 2006;9(1):13-33.


24. Salkovic-Petrisic M, Osmanovic-Barilar J, Brückner MK, Hoyer S, Arendt T, Riederer P. Cerebral amyloid angiopathy in streptozotocin rat model of sporadic Alzheimer's disease: a long-term follow up study. Journal of Neural Transmission 2011;8(5):765-772. PMID: 21533606.


25. Jung SW, Han OK, Kim SJ. Increased expression of β amyloid precursor gene in the hippocampus of streptozotocin- induced diabetic mice with memory deficit and anxiety induction. Journal of Neural Transmission 2010;117:1411-1418. PMID: 21069392.



26. Cho JY, Hwang DY, Kang TS, Shin DH, Hwang JH, Lim CH, Lee SH, Lim HJ, Min SH, Seo SJ, Song YS, Nam KT, Lee KS, Cho JS, Kim YK. Use of NSE/PS2m-transgenic mice in the study of the protective effect of exercise on Alzheimer's disease. Journal of Sports Science and Medicine 2003;21(11):943-51.
27. Um HS, Kang EB, Leem YH, Cho IH, Yang CH, Chae KR, Hwang DY, Cho JY. Exercise training acts as a therapeutic strategy for reduction of the pathogenic phenotypes for Alzheimer's disease in an NSE/APPswtransgenic model. International Journal of Molecular Medicine 2008;22(4):529-539. PMID: 18813861.

28. Leem YH, Lim HJ, Shim SB, Cho JY, Kim BS, Han PL. Repression of tau hyperphosphorylation by chronic endurance exercise in aged transgenic mouse model of tauopathies. J Neurosci Res 2009;87(11):2561-2570. PMID: 19360903.


29. Cho JY, Um HS, Kang EB, Cho IH, Kim CH, Cho JS, Hwang DY. The combination of exercise training and alpha-lipoic acid treatment has therapeutic effects on the pathogenic phenotypes of Alzheimer’s disease in NSE/APPsw-transgenic mice. Int J Mol Med 2010;25(3):337-346. PMID: 20127037.

30. Um HS, Kang EB, Koo JH, Kim HT, Jin-Lee , Kim EJ, Yang CH, An GY, Cho IH, Cho JY. Treadmill exercise represses neuronal cell death in an aged transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Neurosci Res 2011;69(2):161-173. PMID: 20969897.


31. Leem YH, Lee YI, Son HJ, Lee SH. Chronic exercise ameliorates the neuroinflammation in mice carrying NSE/htau23. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2011;406(3):359-65. PMID: 21329662.


32. Kang EB, Kwon IS, Koo JH, Kim EJ, Kim CH, Lee J, Yang CH, Lee YI, Cho IH. Treadmill exercise represses neuronal cell death and inflammation during Aβ-induced ER stress byregulating unfolded protein response in aged presenilin 2 mutant mice. Cho JYApoptosis 2013;18(11):1332-1347.
33. Widegren U, Ryder JW, Zierath JR. Mitogen-activated protein kinase signal transduction in skeletal muscle: effects of exercise and muscle contraction. Acta Physiologica Scandinavica 2001;172(3):227-238. PMID: 11472310.


34. Gleeson M. Immune function in sport and exercise. Journal of Applied Physiology 2007;103(2):693-9. PMID: 17303714.


35. Carmody RJ, Chen YH. Nuclear factor-kappaB: activation and regulation during toll-like receptor signaling. Cell MolImmunol 2007;4(1):31-41.
36. Pandey S, Agrawal DK. Immunobiology of Toll-like receptors: emerging trends. Immunology and Cell Biology 2006;84:333-341. PMID: 16834572.


37. Bankers-Fulbright JL, Kalli KR, McKean DJ. Interleukin-1 signal transduction. Life Sci 1996;59(2):61-83. PMID: 8699924.


38. Kock A, Schwarz T, Kirnbauer R, Urbanski A, Perry P, Ansel JC, Luger TA. Human keratinocytes are a source for tumor necrosis factor α: evidence for synthesis and release upon stimulation with endotoxin or ultraviolet light. J Exp Med 1990;172:1609-1614. PMID: 2258696.




39. Paxinos G, Watson C. The rat brain in sterotaxic coordinates. New York: Avademic Press. Aging (milano). 1998. 2(3):p. 245-58.
40. Sharma M, Gupta YK. Effect of chronic treatment of melatonin on learning, memory and oxidative deficiencies induced by intracerebroventricularstreptozotocin in rats. Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior 2001;70(2-3):325-31.

41. Kim HB, Jang MH, Shin MC, Lim BV, Kim YP, Kim KJ, Kim EH, Kim CJ. Treadmill exercise increases cell proliferation in dentate gyrus of rats with streptozotocininduced diabetes. Journal of Diabetic Complications 2003;17:29-33.

42. Lee HH, Yoon JH, Jeong IG, Kim SH, Kim BK, Shin MS, Ko IG, Sung YH, Kim CJ. Effects of exercise intensity on hippocampal cell proliferation and BDNF expression in intracerebroventricularstreptozotocin inducedmemory impairment in rats. Exercise Science 2009;18(4):475-488.
43. Rodrigues L, Dutra MF, Ilha J, Biasibetti R, Quincozes-Santos A, Leite MC, Marcuzzo S, Achaval M, Gonçalves CA. Treadmill training restores spatial cognitive deficits and neurochemical alterations in the hippocampus of rats submitted to an intracerebroventricular administration of streptozotocin. Journal of Neural Transmission 2010;117(11):1295-1305. PMID: 20953641.



44. Park JB. Activation of microglia by amyloid-β peptide. The Journals of Gerontology 2006;16(1):25-30.
45. Salkovic-Petrisic M, Osmanovic-Barilar J, Brückner MK, Hoyer S, Arendt T, Riederer P. Cerebral amyloid angiopathy in streptozotocin rat model of sporadic Alzheimer's disease: a long-term follow up study. Journal of Neural Transmission 2011;118(5):765-772. PMID: 21533606.



46. Heneka MT, O'Banion MK. Inflammatory processes in Alzheimer's disease. Journal of Neuroimmunology 2007;184:69-91. PMID: 17222916.


47. Hoshino K, Kaisho T, Iwabe T, Takeuchi O, Akira S. Differential involvement of IFN-β in Toll-like receptorstimulated dendritic cell activation. International Journal of Immunology 2002;14(10):1225-1231.


48. Toshchakov V, Jones BW, Perera PY. LR4, but not TLR2, mediates IFN-β-induced STATIα/β-dependent gene expression in macrophages. Nature Immunology 2002;392-398. PMID: 11896392.


49. Jin JJ, Kim HD, Maxwell JA, Li L, Fukuchi K. Toll-like receptor 4-dependent upregulation of cytokines in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Journal of Neuroinflammation 2008;5:23PMID: 18510752.

50. Zanchi NE, Lira FS, de SiqueiraFilho MA, Rosa JC, de Oliveira Carvalho CR, Seelaender M, Santos RV, Lancha AH Jr. Chronic low frequency/low volume resistance training reduces pro-inflammatory cytokine protein levels and TLR4 mRNA in rat skeletal muscle. European Journal of Applied Physiology 2010;106:415-423. PMID: 19306017.


51. Lambert CP, Wright NR, Finck BN, Villareal DT. Exercise but not diet-induced weight loss decreases skeletal muscle inflammatory gene expression in frail obese elderly persons. Journal of Applied Physiology 2008;105(2):473-478. PMID: 18535122.

52. Lima-Cabello E, Cuevas MJ, Garatachea N, Baldini M, Almar M, González-Gallego J. Eccentric exercise induces nitric oxide synthase expression through nuclear factorkappa B modulation in rat skeletal muscle. Journal of Applied Physiology 2010;108(3):575-583. PMID: 20044475.

53. Lovatel G A, Elsner VR, Bertoldi K, Vanzella C, Moysés Fdos S, Vizuete A, Spindler C, Cechinel LR, Netto CA, Muotri AR, Siqueira IR. Treadmill exercise induces age-related changes in aversive memory, neuroinflammatory and epigenetic processes in the rat hippocampus. Neurobiology of Learning and Memory 2013;101:94-102. PMID: 23357282.

Fig. 1.
Effect of treadmill exercise on cognitive function in STZ-induced animal model of AD. (A) Patterns of escape latency and escape distance. The escape latency and escape distance significantly decreased in the STZ-Exe, compared with STZ-Con groups. (B) Patterns of swimming the Sham-Con, STZ-Con and STZ-Exe. Values are expressed as means ± standard deviation.
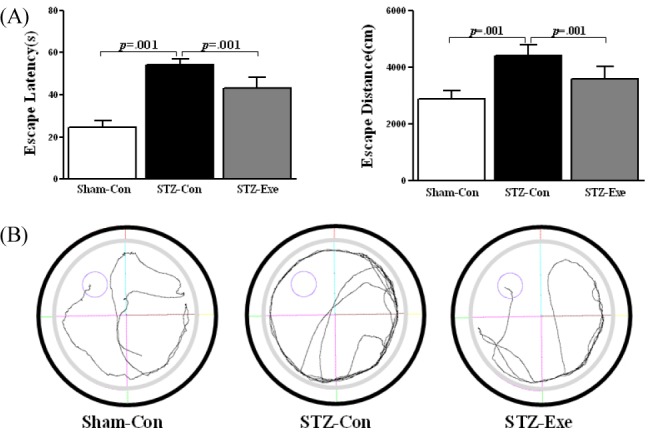
Fig. 2.
Effect of treadmill exercise on Aβ level in the cortex of STZ-induced animal model of AD. (A-B) Expression of Aβ level in the cortex was analyzed by Westernblot and immuno staining analysis. (A) Level of Aβ was significantly decreased in STZ-Exe compared to STZ-Con. (B) Low-level staining of Aβ in the cortex is seen in STZ-Exe. Intensive deposition of Aβ immune reactivity is unique to STZ-Con in the cortex. Values are expressed as means ± standard deviation.
Fig. 3.
Effect of treadmill exercise on TLR4 and NF-κB in the cortex of STZ-induced animal model of AD. (A) Expression of TLR4 and NF-κB in the cortex was analyzed by Western blot. (B-C) TLR4 and NF-κB were significantly decreased in STZ-Exe compared to STZ-Con. Values are presented as means ± standard deviation.

Fig. 4.
Effect of treadmill exercise on TNF-α and IL-1α in the cortex of STZ-induced animal model of AD. (A) Expression of TNF-α and IL-1α in the cortex was analyzed by Western blot. (B-C) TNF-α and IL-1α were significantly decreased in STZ-Exe compared to STZ-Con. Values are presented as means ± standard deviation.
- TOOLS
-
METRICS

-
- 19 Crossref
- 3,482 View
- 12 Download
- Related articles in Phys Act Nutr