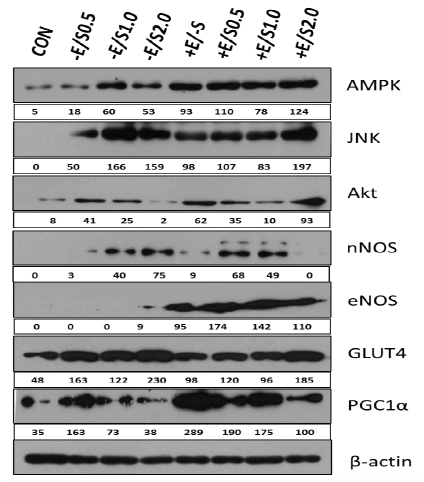
1.
Booth FW, Lees SJ. Fundamental questions about genes, inactivity, and chronic diseases. Physiol Genomics. 2007;28:146-57.

Booth FW, Lees SJ. Fundamental questions about genes, inactivity, and chronic diseases.
Physiol Genomics 2007;28:146-57. PMID:
10.1152/physiolgenomics.00174.2006. PMID:
17032813.
2.
Booth FW, Thomason DB. Molecular and cellular adaptation of muscle in response to exercise: perspectives of various models. Physiol Rev. 1991;71:541-85.

Booth FW, Thomason DB. Molecular and cellular adaptation of muscle in response to exercise: perspectives of various models.
Physiol Rev 1991;71:541-85. PMID:
10.1152/physrev.1991.71.2.541. PMID:
2006222.
3.
Fl├╝ck M, Hoppeler H. Molecular basis of skeletal muscle plasticity - from gene to form and function. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 2003;146:159-216.

Fl├╝ck M, Hoppeler H. Molecular basis of skeletal muscle plasticity - from gene to form and function.
Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol 2003;146:159-216. PMID:
12605307.
4.
Fl├╝ck M. Functional, structural and molecular plasticity of mammalian skeletal muscle in response to exercise stimuli. J Exp Biol. 2006;209:2239-48.

Fl├╝ck M. Functional, structural and molecular plasticity of mammalian skeletal muscle in response to exercise stimuli.
J Exp Biol 2006;209:2239-48. PMID:
16731801.
5.
Gregory AJ, Fitch RW. Sports medicine: performance-enhancing drugs. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2007;54:797-806.

Gregory AJ, Fitch RW. Sports medicine: performance-enhancing drugs.
Pediatr Clin North Am 2007;54:797-806. PMID:
17723878.
6.
McClung M, Collins D. "Because I know it will!": placebo effects of an ergogenic aid on athletic performance. J Sport Exerc Psychol. 2007;29:382-94.

McClung M, Collins D. "Because I know it will!": placebo effects of an ergogenic aid on athletic performance.
J Sport Exerc Psychol 2007;29:382-94. PMID:
10.1123/jsep.29.3.382. PMID:
17876973.
7.
Ito A, Yamamoto Y, Sato M, Ikeda K, Yamamoto M, Fujita H, Nagamori E, Kawabe Y, Kamihira M. Induction of functional tissue-engineered skeletal muscle constructs by defined electrical stimulation. Sci Rep. 2014;24:4781.


Ito A, Yamamoto Y, Sato M, Ikeda K, Yamamoto M, Fujita H, Nagamori E, Kawabe Y, Kamihira M. Induction of functional tissue-engineered skeletal muscle constructs by defined electrical stimulation.
Sci Rep 2014;24:4781.
8.
Nikoli─ć N, Bakke SS, Kase ET, Rudberg I, Flo Halle I, Rustan AC, Thoresen GH, Aas V. Electrical pulse stimulation of cultured human skeletal muscle cells as an in vitro model of exercise. PLoS One. 2012;7:e33203.

Nikoli─ć N, Bakke SS, Kase ET, Rudberg I, Flo Halle I. Rustan AC, Thoresen GH, Aas V. Electrical pulse stimulation of cultured human skeletal muscle cells as an in vitro model of exercise.
PLoS One 2012;7:e33203PMID:
22457744.
9.
Holloszy JO, Booth FW. Biochemical adaptations to endurance exercise in muscle. Annu Rev Physiol. 1976;38:273-91.

Holloszy JO, Booth FW. Biochemical adaptations to endurance exercise in muscle.
Annu Rev Physiol 1976;38:273-91. PMID:
10.1146/annurev.ph.38.030176.001421. PMID:
130825.
10.
Holloszy JO, Coyle EF. Adaptations of skeletal muscle to endurance exercise and their metabolic consequences. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1984;56:831-8.

Holloszy JO, Coyle EF. Adaptations of skeletal muscle to endurance exercise and their metabolic consequences.
J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol 1984;56:831-8. PMID:
10.1152/jappl.1984.56.4.831. PMID:
6373687.
11.
Coffey VG, Hawley JA. The molecular bases of training adaptation. Sports Med. 2007;37:737-63.

Coffey VG, Hawley JA. The molecular bases of training adaptation.
Sports Med 2007;37:737-63. PMID:
10.2165/00007256-200737090-00001. PMID:
17722947.
12.
Chow LS, Greenlund LJ, Asmann YW, Short KR, McCrady SK, Levine JA, Nair KS. Impact of endurance training on murine spontaneous activity, muscle mitochondrial DNA abundance, gene transcripts, and function. J Appl Physiol. 2007;102:1078-89.

Chow LS, Greenlund LJ, Asmann YW, Short KR, McCrady SK, Levine JA, Nair KS. Impact of endurance training on murine spontaneous activity, muscle mitochondrial DNA abundance, gene transcripts, and function.
J Appl Physiol 2007;102:1078-89. PMID:
10.1152/japplphysiol.00791.2006. PMID:
17110513.
13.
Visek WJ. Arginine needs, physiological state and usual diets. A reevaluation, J Nutr. 1986;116:36-46.


Visek WJ. Arginine needs, physiological state and usual diets. A reevaluation.
J Nutr 1986;116:36-46. PMID:
10.1093/jn/116.1.36. PMID:
3080558.
14.
Chromiak JA, Antonio J. Use of amino acids as growth hormone-releasing agents by athletes. Nutrition. 2002;18:657-61.

Chromiak JA, Antonio J. Use of amino acids as growth hormone-releasing agents by athletes.
Nutrition 2002;18:657-61. PMID:
10.1016/s0899-9007(02)00807-9. PMID:
12093449.
15.
Campbell BI, La Bounty PM, Roberts M. The ergogenic potential of arginine. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2001;31:35-8.


Campbell BI, La Bounty PM, Roberts M. The ergogenic potential of arginine.
J Int Soc Sports Nutr 2001;31:35-8.
16.
Bredt DS, Hwang PM, Snyder SH. Localization of nitric oxide synthase indicating a neural role for nitric oxide. Nature. 1990;347:768-70.


Bredt DS, Hwang PM, Snyder SH. Localization of nitric oxide synthase indicating a neural role for nitric oxide.
Nature 1990;347:768-70. PMID:
10.1038/347768a0. PMID:
1700301.
17.
Nathan C, Xie QW. Nitric oxide synthases: roles, tolls, and controls. Cell. 1994;78:915-8.

Nathan C, Xie QW. Nitric oxide synthases: roles, tolls, and controls.
Cell 1994;78:915-8. PMID:
10.1016/0092-8674(94)90266-6. PMID:
7522969.
18.
Gastom B, Stamler J. Biochemistry of nitric oxide. In: Nitric Oxide and Infection. New York: Plenum, 1999;37-53.
Gastom B, Stamler JBiochemistry of nitric oxide. In: Nitric Oxide and Infection. New York: Plenum. 1999. p. 37-53.
19.
Alderton WK, Cooper CE, Knowles RG. Nitric oxide synthases: structure, function and inhibition. Biochem J. 2001;357:593-615.


Alderton WK, Cooper CE, Knowles RG. Nitric oxide synthases: structure, function and inhibition.
Biochem J 2001;357:593-615. PMID:
10.1042/0264-6021:3570593. PMID:
11463332.
20.
Rubinstein I, Abassi Z, Coleman R, Milman F, Winaver J, Better OS. Involvement of nitric oxide system in experimental muscle crush injury. J Clin Invest. 1988;101:1325-33.

Rubinstein I, Abassi Z, Coleman R, Milman F, Winaver J, Better OS. Involvement of nitric oxide system in experimental muscle crush injury.
J Clin Invest 1988;101:1325-33.
21.
Balon TW, Nadler JL. Evidence that nitric oxide increases glucose transport in skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol. 1997;82:359-63.

Balon TW, Nadler JL. Evidence that nitric oxide increases glucose transport in skeletal muscle.
J Appl Physiol 1997;82:359-63. PMID:
10.1152/jappl.1997.82.1.359. PMID:
9029239.
22.
Capanni C, Squarzoni S, Petrini S, Villanova M, Muscari C, Maraldi NM, Guarnieri C, Caldarera CM. Increase of neuronal nitric oxide synthase in rat skeletal muscle during ageing. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1998;245:216-9.

Capanni C, Squarzoni S, Petrini S, Villanova M, Muscari C, Maraldi NM, Guarnieri C, Caldarera CM. Increase of neuronal nitric oxide synthase in rat skeletal muscle during ageing.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1998;245:216-9. PMID:
10.1006/bbrc.1998.8404. PMID:
9535811.
23.
Baron AD, Brechtel-Hook G, Johnson A, Cronin J, Leaming R, Steinberg HO. Effect of perfusion rate on the time course of insulin-mediated skeletal muscle glucose uptake. Am J Physiol. 1996;271:E1067-72.

Baron AD, Brechtel-Hook G, Johnson A, Cronin J, Leaming R, Steinberg HO. Effect of perfusion rate on the time course of insulin-mediated skeletal muscle glucose uptake.
Am J Physiol 1996;271:E1067-72. PMID:
10.1152/ajpendo.1996.271.6.e1067. PMID:
8997227.
24.
Tidball JG, Lavergne E, Lau KS, Spencer MJ, Stull JT, Wehling M. Mechanical loading regulates NOS expression and activity in developing and adult skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol. 1998;275:C260-6.

Tidball JG, Lavergne E, Lau KS, Spencer MJ, Stull JT, Wehling M. Mechanical loading regulates NOS expression and activity in developing and adult skeletal muscle.
Am J Physiol 1998;275:C260-6. PMID:
10.1152/ajpcell.1998.275.1.c260. PMID:
9688857.
25.
Riede UN, F├Črstermann U, Drexler H. Inducible nitric oxide synthase in skeletal muscle of patients with chronic heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1998;32:964-9.

Riede UN, F├Črstermann U, Drexler H. Inducible nitric oxide synthase in skeletal muscle of patients with chronic heart failure.
J Am Coll Cardiol 1998;32:964-9. PMID:
10.1016/s0735-1097(98)00335-0. PMID:
9768718.
26.
Adams V, Jiang H, Yu J, M├Čbius-Winkler S, Fiehn E, Linke A, Weigl C, Schuler G, Hambrecht R. Apoptosis in skeletal myocytes of patients with chronic heart failure is associated with exercise intolerance. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1999;33:959-65.

Adams V, Jiang H, Yu J, M├Čbius-Winkler S, Fiehn E, Linke A, Weigl C, Schuler G, Hambrecht R. Apoptosis in skeletal myocytes of patients with chronic heart failure is associated with exercise intolerance.
J Am Coll Cardiol 1999;33:959-65. PMID:
10.1016/s0735-1097(98)00626-3. PMID:
10091822.
27.
Tews DS, Goebel HH. Cell death and oxidative damage in inflammatory myopathies. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1998;87:240-7.

Tews DS, Goebel HH. Cell death and oxidative damage in inflammatory myopathies.
Clin Immunol Immunopathol 1998;87:240-7. PMID:
10.1006/clin.1998.4527. PMID:
9646833.
28.
Boczkowski J, Lanone S, Ungureanu-Longrois D, Danialou G, Fournier T, Aubier M. Induction of diaphragmatic nitric oxide synthase after endotoxin administration in rats: role on diaphragmatic contractile dysfunction. J Clin Invest. 1996;98:1550-9.

Boczkowski J, Lanone S, Ungureanu-Longrois D, Danialou G, Fournier T, Aubier M. Induction of diaphragmatic nitric oxide synthase after endotoxin administration in rats: role on diaphragmatic contractile dysfunction.
J Clin Invest 1996;98:1550-9. PMID:
10.1172/jci118948. PMID:
8833903.
29.
El Dwairi Q, Guo Y, Comtois A, Zhu E, Greenwood MT, Bredt DS, Hussain SN. Ontogenesis of nitric oxide synthases in the ventilatory muscles. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1998;18:844-52.

El Dwairi Q, Guo Y, Comtois A, Zhu E, Greenwood MT, Bredt DS, Hussain SN. Ontogenesis of nitric oxide synthases in the ventilatory muscles.
Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 1998;18:844-52. PMID:
10.1165/ajrcmb.18.6.3109. PMID:
9618389.
30.
Nagasaki A, Gotoh T, Takeya M, Yu Y, Takiguchi M, Matsuzaki H, Takatsuki K, Mori M. Coinduction of nitric oxide synthase, argininosuccinate synthetase, and argininosuccinate lyase in lipopolysaccharide-treated rats. RNA blot, immunoblot, and immunohistochemical analyses. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:2658-62.

Nagasaki A, Gotoh T, Takeya M, Yu Y, Takiguchi M, Matsuzaki H, Takatsuki K, Mori M. Coinduction of nitric oxide synthase, argininosuccinate synthetase, and argininosuccinate lyase in lipopolysaccharide-treated rats. RNA blot, immunoblot, and immunohistochemical analyses.
J Biol Chem 1996;271:2658-62. PMID:
10.1074/jbc.271.5.2658. PMID:
8576237.
31.
Thompson M, Becker L, Bryant D, Williams G, Levin D, Margraf L, Giroir BP. Expression of the inducible nitric oxide synthase gene in diaphragm and skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol. 1996;81:2415-20.

Thompson M, Becker L, Bryant D, Williams G, Levin D, Margraf L, Giroir BP. Expression of the inducible nitric oxide synthase gene in diaphragm and skeletal muscle.
J Appl Physiol 1996;81:2415-20. PMID:
10.1152/jappl.1996.81.6.2415. PMID:
9018487.
32.
Hussain SN, Giaid A, El Dawiri Q, Sakkal D, Hattori R, Guo Y. Expression of nitric oxide synthases and GTP cyclohydrolase I in the ventilatory and limb muscles during endotoxemia. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1997;17:173-80.

Hussain SN, Giaid A, El Dawiri Q, Sakkal D, Hattori R, Guo Y. Expression of nitric oxide synthases and GTP cyclohydrolase I in the ventilatory and limb muscles during endotoxemia.
Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 1997;17:173-80. PMID:
10.1165/ajrcmb.17.2.2612. PMID:
9271305.
33.
Murrant CL, Frisbee JC, Barclay JK. The effect of nitric oxide and endothelin on skeletal muscle contractility changes when stimulation is altered. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1997;75:414-22.

Murrant CL, Frisbee JC, Barclay JK. The effect of nitric oxide and endothelin on skeletal muscle contractility changes when stimulation is altered.
Can J Physiol Pharmacol 1997;75:414-22. PMID:
10.1139/y97-096. PMID:
9250375.
34.
Hickner RC, Fisher JS, Ehsani AA, Kohrt WM. Role of nitric oxide in skeletal muscle blood flow at rest and during dynamic exercise in humans. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 1997;273: H4010.

Hickner RC, Fisher JS, Ehsani AA, Kohrt WM. Role of nitric oxide in skeletal muscle blood flow at rest and during dynamic exercise in humans.
Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 1997;273:H4010PMID:
10.1152/ajpheart.1997.273.1.h405.
35.
Lee KH, Baek MY, Moon KY, Song WK, Chung CH, Ha DB, Kang MS. Nitric oxide as a messenger molecule for myoblast fusion. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:14371-4.

Lee KH, Baek MY, Moon KY, Song WK, Chung CH, Ha DB, Kang MS. Nitric oxide as a messenger molecule for myoblast fusion.
J Biol Chem 1994;269:14371-4. PMID:
7514168.
36.
Kobzik L, Stringer B, Balligand JL, Reid MB, Stamler JS.Endothelial type nitric oxide synthase in skeletal muscle fibers: mitochondrial relationships. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1995;211:375-81.

Kobzik L, Stringer B, Balligand JL, Reid MB, Stamler JS. Endothelial type nitric oxide synthase in skeletal muscle fibers: mitochondrial relationships.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1995;211:375-81. PMID:
7540837.
37.
Tidball JG, Lavergne E, Lau KS, Spencer MJ, Stull JT, Wehling M. Mechanical loading regulates NOS expression and activity in developing and adult skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 1998;275:C260.

Tidball JG, Lavergne E, Lau KS, Spencer MJ, Stull JT, Wehling M. Mechanical loading regulates NOS expression and activity in developing and adult skeletal muscle.
Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 1998;275:C260PMID:
10.1152/ajpcell.1998.275.1.c260.
38.
He K, Hu J, Yu H, Wang L, Tang F, Gu J, Ge L, Wang H, Li S, Hu P, Jin Y. Stk40 functions as a novel regulator of skeletal muscle differentiation. J Biol Chem. 2016;292:351-60.

He K, Hu J, Yu H, Wang L, Tang F, Gu J, Ge L, Wang H, Li S, Hu P, Jin Y. Stk40 functions as a novel regulator of skeletal muscle differentiation.
J Biol Chem 2016;292:351-60. PMID:
27899448.
39.
Manabe Y, Miyatake S, Takagi M, Nakamura M, Okeda A, Nakano T, Hirshman MF, Goodyear LJ, Fujii NL. Characterization of an acute muscle contraction model using cultured C2C12 myotubes. PLoS One. 2012;7:e52592.

Manabe Y, Miyatake S, Takagi M, Nakamura M, Okeda A, Nakano T, Hirshman MF, Goodyear LJ, Fujii NL. Characterization of an acute muscle contraction model using cultured C2C12 myotubes.
PLoS One 2012;7:e52592PMID:
10.1371/journal.pone.0052592. PMID:
23300713.
40.
Douen AG, Ramlal T, Klip A, Young DA, Cartee GD, Holloszy JO. Exercise-induced increase in glucose transporters in plasma membranes of rat skeletal muscle. Endocrinology. 1989;124:449-54.

Douen AG, Ramlal T, Klip A, Young DA, Cartee GD, Holloszy JO. Exercise-induced increase in glucose transporters in plasma membranes of rat skeletal muscle.
Endocrinology 1989;124:449-54. PMID:
10.1210/endo-124-1-449. PMID:
2642418.
41.
Gulve EA, Cartee GD, Zierath JR, Corpus VM, Holloszy JO. Reversal of enhanced muscle glucose transport after exercise: roles of insulin and glucose. Am J Physiol. 1990;259:E685-91.

Gulve EA, Cartee GD, Zierath JR, Corpus VM, Holloszy JO. Reversal of enhanced muscle glucose transport after exercise: roles of insulin and glucose.
Am J Physiol 1990;259:E685-91. PMID:
10.1152/ajpendo.1990.259.5.e685. PMID:
2240207.
42.
Constable SH, Favier RJ, Cartee GD, Young DA, Holloszy JO. Muscle glucose transport: interactions of in vitro contractions, insulin, and exercise. J Appl Physiol. 1988;64:2329-32.

Constable SH, Favier RJ, Cartee GD, Young DA, Holloszy JO. Muscle glucose transport: interactions of in vitro contractions, insulin, and exercise.
J Appl Physiol 1988;64:2329-32. PMID:
10.1152/jappl.1988.64.6.2329. PMID:
3136124.
43.
Ivy JL. Muscle insulin resistance amended with exercise training: role of GLUT4 expression. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2004;36:1207-11.
Ivy JL. Muscle insulin resistance amended with exercise training: role of GLUT4 expression.
Med Sci Sports Exerc 2004;36:1207-11. PMID:
15235327.
44.
Balon TW, Nadler JL. Nitric oxide release is present from incubated skeletal muscle preparations. J Appl Physiol. 1994;77:2519-21.

Balon TW, Nadler JL. Nitric oxide release is present from incubated skeletal muscle preparations.
J Appl Physiol 1994;77:2519-21. PMID:
10.1152/jappl.1994.77.6.2519. PMID:
7896585.
45.
Mohr S, Stamler JS, Br├╝ne B. Posttranslational modification of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase by S-nitrosylation and subsequent NADH attachment. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:4209-14.

Mohr S, Stamler JS, Br├╝ne B. Posttranslational modification of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase by S-nitrosylation and subsequent NADH attachment.
J Biol Chem 1996;271:4209-14. PMID:
10.1074/jbc.271.8.4209. PMID:
8626764.
46.
Brown GC. Nitric oxide regulates mitochondrial respiration and cell functions by inhibiting cytochrome oxidase. FEBS Lett. 1995;369:136-9.

Brown GC. Nitric oxide regulates mitochondrial respiration and cell functions by inhibiting cytochrome oxidase.
FEBS Lett 1995;369:136-9. PMID:
10.1016/0014-5793(95)00763-y. PMID:
7649245.
47.
Reid MB. Role of nitric oxide in skeletal muscle: synthesis, distribution and functional importance. Acta Physiol Scand. 1998;162:401-9.

Reid MB. Role of nitric oxide in skeletal muscle: synthesis, distribution and functional importance.
Acta Physiol Scand 1998;162:401-9. PMID:
10.1046/j.1365-201x.1998.0303f.x. PMID:
9578386.
48.
Etgen GJ Jr, Jensen J, Wilson CM, Hunt DG, Cushman SW, Ivy JL. Exercise training reverses insulin resistance in muscle by enhanced recruitment of GLUT-4 to the cell surface. Am J Physiol. 1997;272:E864-9.

Etgen GJ Jr, Jensen J, Wilson CM, Hunt DG, Cushman SW, Ivy JL. Exercise training reverses insulin resistance in muscle by enhanced recruitment of GLUT-4 to the cell surface.
Am J Physiol 1997;272:E864-9. PMID:
10.1152/ajpendo.1997.272.5.e864. PMID:
9176187.
49.
Kingwell BA, Formosa M, Muhlmann M, Bradley SJ, McConell GK. Nitric oxide synthase inhibition reduces glucose uptake during exercise in individuals with type 2 diabetes more than in control subjects. Diabetes. 2002;51:2572-80.

Kingwell BA, Formosa M, Muhlmann M, Bradley SJ, McConell GK. Nitric oxide synthase inhibition reduces glucose uptake during exercise in individuals with type 2 diabetes more than in control subjects.
Diabetes 2002;51:2572-80. PMID:
10.2337/diabetes.51.8.2572. PMID:
12145173.